
Apr 8, 2019
First published on ScienceDaily.com
The full financial cost of a heart attack or stroke is twice as much as the medical costs when lost work time for patients and caregivers is included.
That’s the finding of research published today, World Health Day, in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 The study concludes that victims of heart attack and stroke who return to work are 25% less productive in their first year back.
In the year after the event, heart patients lost 59 workdays and caregivers lost 11 workdays, for an average cost of €13,953, and ranging from €6,641 to €23,160 depending on the country. After stroke, 56 workdays were lost by patients and 12 by caregivers, for an average €13,773, ranging from €10,469 to €20,215.
Study author Professor Kornelia Kotseva, of Imperial College London, UK, said: “Patients in our study returned to work, meaning their events were relatively mild. Some still had to change jobs or careers, or work less, and caregivers lost around 5% of work time. Not included in our study are those with more severe events who quit work altogether and presumably need even more help from family and friends.”
The study enrolled 394 patients from seven European countries — 196 with acute coronary syndrome (86% heart attack, 14% unstable chest pain) and 198 with stroke — who returned to work 3 to 12 months after the event. Patients completed a questionnaire2,3 during a visit to a cardiologist, neurologist, or stroke physician. Hours lost were valued according to country labour costs in 2018. The average age of patients was 53 years.
According to published estimates for Europe, the direct medical costs of acute coronary syndrome are €1,547 to €18,642, and €5,575 to €31,274 for stroke.4 “This is the metric commonly used to estimate the costs of medical conditions while indirect costs from productivity loss are often not taken into account by clinicians, payers or policymakers,” said Professor Kotseva. “Taken together, the actual burden on society is more than twice the amount previously reported.”
You can read the full article here.

Apr 7, 2019
First published on ScienceDaily.com
Newly developed treatment strategies can minimize the size of a patient’s stroke and, in many cases, change what would have been a life-altering cerebrovascular event into a minor one with the prospect of excellent recovery. But these therapies are time sensitive — delays in seeking care can put them out of reach. Each year in the U.S., 795,000 patients will have a stroke and approximately 70 percent of them will arrive at the hospital more than six hours after the onset of symptoms. Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital examined how social networks may influence delays in arrival times for patients experiencing the symptoms of a stroke. Paradoxically, they found that patients with closer-knit social networks, including family members and spouses, were more likely to delay seeking hospital care whereas those with a more dispersed network of acquaintances were more likely to seek care faster. The team’s analysis is published in Nature Communications.
“Closed networks are like echo chambers in which there is a tendency for everyone to agree to watch and wait,” said corresponding author Amar Dhand, MD, DPhil, of the Department of Neurology at the Brigham. “A major problem in stroke care is patients’ delayed arrival to the hospital, and we show that this problem is related to the influence of patients’ social networks.”
Dhand and colleagues surveyed 175 patients within five days of suffering from a stroke. They collected information from each participant about personal social networks, creating network maps. The team focused on patients with milder symptoms because this population is at higher risk for delay and were able to engage in the survey during hospitalization.
You can read the full article here.
Apr 4, 2019
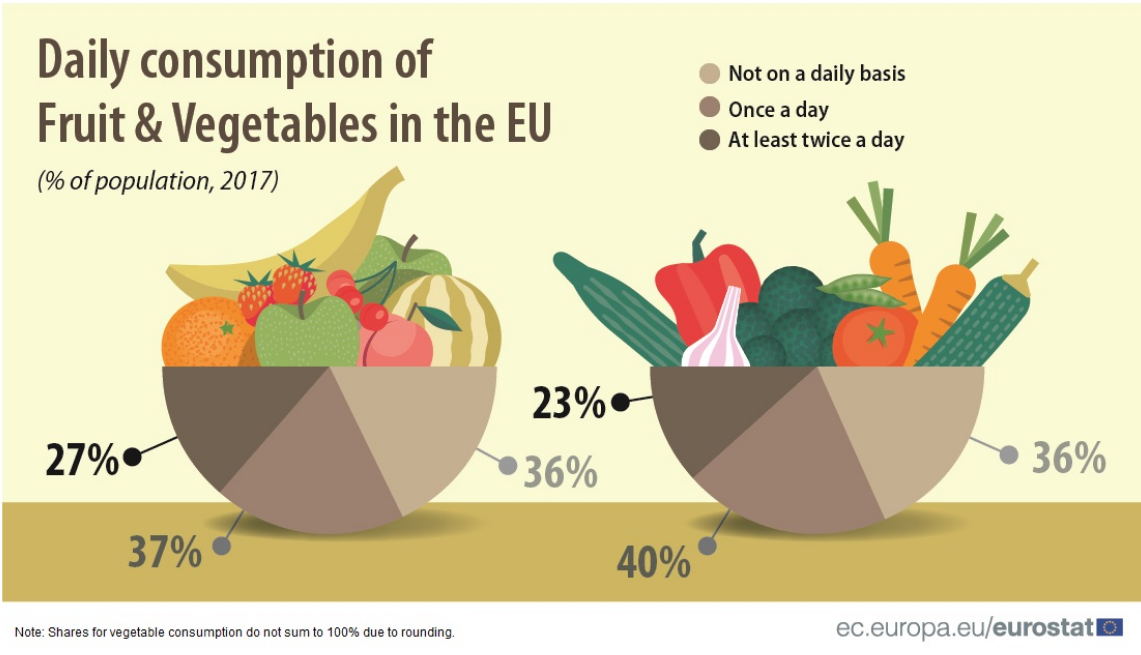
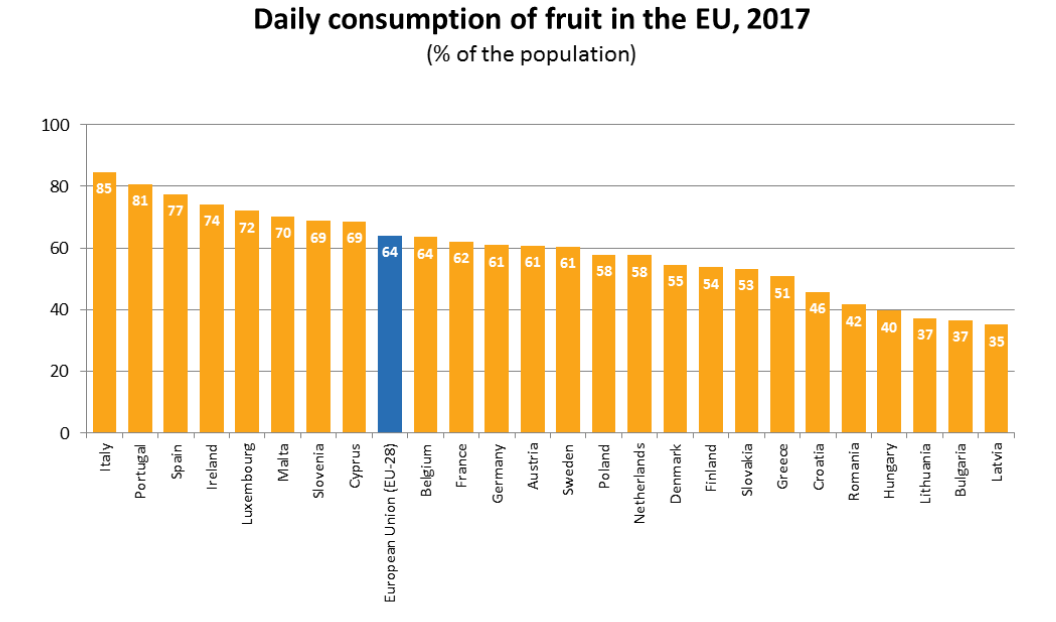
In 2017, around 1 in 4 people (27 %) ate fruit at least twice a day, according to a survey of the European Union (EU) population. A further 37 % of the EU population ate fruit once a day and the remaining 36 % ate fruit either less frequently or not at all during a typical week. Compared with fruit consumption, a slightly smaller proportion (23 %) of the EU population ate vegetables at least twice a day, and a slightly higher proportion (40 %) ate vegetables once a day. Among the EU Member States, daily intake of fruit was most prevalent in Italy (85 % of the population) and in Portugal (81 %).
The source data are here.
In contrast, in three Member States less than 40 % of the population ate fruit on a daily basis: Latvia (35 %), Bulgaria and Lithuania (both 37 %). When it comes to vegetable consumption in the Member States, Ireland and Belgium had the highest proportion of the population who ate vegetables at least once a day (both 84 %). While in most Member States between 50 % and 80 % of the population reported that they ate vegetables daily, there were five Member States where the proportion was below 50 %: Hungary (30 %), Romania (41 %), Latvia (44 %), Lithuania and Bulgaria (both 45 %).
For more information from this report, please click here.

Mar 28, 2019
Brussels, 28 March 2019- The Stroke Alliance for Europe (SAFE) organised today the event ‘Joining forces to prevent and control non-communicable diseases: The role of policy in tackling stroke’, under the patronage of the Romanian Presidency of the Council of the European Union, in Brussels, at the European Committee of the Regions. The event was organised by SAFE in collaboration with the European Stroke Organisation and the Romanian National Stroke Association.
The panel participants have put many proposals on the table. The most important request is for forming a stroke related sub-group for the purpose of facilitating the implementation of the Stroke Action Plan for Europe, the same as has been done for cancer and mental health.
As Jon Barrick, SAFE President stressed in his opening speech, the topic discussed today is of extreme importance: Stroke is the second most common cause of death in Europe, with nearly one hundred thousand (988,000) deaths each year[1]. In Europe, over 13% of women and 9% of men die from this disease (data from the MEP Hearth Group of the European Parliament).
 In 2018, SAFE and ESO released the “Stoke Action Plan for Europe 2018-2030”, which proposes a holistic approach to stroke management, from prevention to acute care, rehabilitation and life after stroke. The report sets out minimum targets to be reached by every European country, to equilibrate the quality of care across Europe.
In 2018, SAFE and ESO released the “Stoke Action Plan for Europe 2018-2030”, which proposes a holistic approach to stroke management, from prevention to acute care, rehabilitation and life after stroke. The report sets out minimum targets to be reached by every European country, to equilibrate the quality of care across Europe.
“Romania is definitely trying to put an end to inequalities in stroke care across the country, and we hope to see the same thing achieved at European level” said Tiberius-Marius Brădățan, Secretary of State, Ministry of Health of Romania. “We think that this is now possible thanks to the Stroke Action Plan for Europe that SAFE and ESO have released. If implemented, the Action Plan will underpin the step change in stroke care that is required to reduce the devastating impact that this condition has on individuals, their families and Member States’ economies.”
Effective healthcare planning and adequate resource allocation across Europe is needed to deal with this public health challenge, taking into account that the emotional and financial burden of stroke is largely borne by stroke survivors themselves and their families.
“Stroke remains a major cause of disability and death, but the opportunities to curb the effects of stroke have dramatically improved”- said Prof. Bo Norrving, who chaired the European Action Plan for Stroke 2018-30 steering committee, adding “While we are discussing the implementation of the European Stroke Action Plan, strokes continue to occur, and patients continue to get substandard care – becoming disabled or dying. Time to go from table to practice is now!”
Sorin Tuță, Vice-president of the Romanian National Stroke Association (ANRS), said that although Romania faces 61.500 new strokes each year, things have significantly improved in the past several years, especially in the domain of the acute stroke treatment, with 32 new stroke ready hospitals in 2019.

SAFE President and the representatives from the Romanian EU Presidency
“Romanian Registry for Interventional Treatment in Stroke was established in 2014 and stroke patients are treated almost exclusively by neurologists” stressed out Cristina Tiu, President Elect of the Romanian Neurology Society.
Prof. Tiina Laatikainen, from the Institute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, Finland, said that, even though the emergency care well organized and those hospitals not having neurologists 24/7 achieve consultancy by telestroke service, there are still challenges, such as endovascular treatments not available 24/7 in the whole country due to lack of angioradiologists, less than 15 % of patients achieve adequate rehabilitation and every fourth working aged stroke patient do not return to work (disability pension).
Thanking all discussion participants and the EU Romanian Presidency and the Committee of Regions for their support, Jon Barrick concluded the session by saying: “We have the scientific community and patients aligned. We have the will of European, national and regional decision-makers, and industry partners who are here today to give their support to future activities aimed at improving stroke prevention, treatment and research. I would therefore like to call upon the future European leaders, and upon the Member States, to work together to achieve the 2030 goals as set by the “2030 Stoke Action Plan for Europe.”

[1] Stroke is also the second most common cause of death in the EU, with over 425,000 deaths each year.

Mar 25, 2019
First published on ScienceDaily.com
Our genes may have a bearing not only on our stroke risk, but probably also on how well we recover after stroke. For the first time, in international collaboration, scientists at the University of Gothenburg and elsewhere have identified common genetic variants that are associated with outcome after ischemic stroke.
The study, a meta-analysis of 12 international stroke studies, was led by research groups at two Swedish universities: Gothenburg and Lund. The study comprised more than 6,000 patients with ischemic stroke, the most common form of stroke, in which a blood clot causes a lack of oxygen in a region of the brain. Stroke can also be caused by a hemorrhage in the brain.
For the study, the patients were divided into two groups depending on their outcome at three months after ischemic stroke. One group was composed of people who had not survived and those who were dependent on help from others to cope with activities of daily living.
Those assigned to the second group were, three months after their stroke onset, able to cope unaided. By comparing analyses of the patients’ genomes, the researchers were able to find several different genetic variants that appear to have played a part in the patients’ outcomes.
“One of the common genetic variants we found was significant — that is, clearly associated with a worse outcome in the large volumes of data we were able to access,” says Annie Pedersen, a PhD student at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, one of the lead authors of the study.
The genetic variant identified can be linked to another gene that is part of a major process involved in brain plasticity, which is the nerve cells’ ability to adapt and take over functions when other nerve cells in the brain die.
The study took into account several other factors — age, sex and the extent of the patient’s brain damage — that can also affect outcome after stroke. After adjustment for these factors, the association remained between the genetic variant and elevated risk of being in the group of patients who still, three months after the stroke onset, were unable to manage without assistance.
“Even if two patients seem to have the same prospects of recovering, their outcomes can be different. Studies on animals have indicated that there are genes that may contribute to the explanation, and we’ve now found support for them in humans as well,” Pedersen says.
Our limited knowledge of why some patients recover well while others incur lasting functional impairments after the same type of stroke has made it difficult to develop new treatment methods, thinks Professor Christina Jern of Sahlgrenska Academy, who ran the study in collaboration with Professor Arne Lindgren of Lund University.
“In the long run we hope the research may enable us to identify new targets for medication that might help to improve poststroke outcome, but there’s a lot of research to be done before we get there,” Jern says.
You can read the full article here.

Mar 20, 2019
First published on ScienceDaily.com
Recent reductions in hospitalization and death due to stroke extend to both black and white Medicare beneficiaries, reports a study in the April issue of Medical Care.
The reductions in mortality after initial stroke have been even greater in black Medicare patients, according to the new research by Margaret C. Fang, MD, MPH, of the University of California, San Francisco, and colleagues. Dr. Fang comments,” Despite these promising trends, our study also found that black men and women continue to be at higher risk for stroke than white patients.”
Stroke Risks Decline Over 25 Years — Trends Linked to Improving Risk Factors
Using Medicare data from 1988 to 2013, the researchers analyzed trends in hospitalization and mortality after an initial stroke in black or white men and women aged 65 or older. The study included more than 1 million hospitalizations for ischemic stroke, caused by blockage or narrowing of the brain blood vessels; and nearly 150,000 hospitalizations for hemorrhagic stroke, caused by bleeding into or around the brain.
Over the 25-year study period, hospitalizations for stroke decreased for both black and white patients. Adjusted for age, ischemic stroke risk decreased from 1,185 to 551 per 100,000 Medicare beneficiaries among black men and from 932 to 407 per 100,000 among white men. Risk fell from 1,222 to 641 per 100,000 for black women and from 892 to 466 per 100,000 for white women.
Mortality after ischemic stroke also fell, with greater reductions in black patients. Risk of death within 30 days after ischemic stroke decreased from approximately 16 to 8 percent in black men and from 16 to 12 percent in white men. Ischemic stroke mortality declined from about 14 to 9 percent in black women versus 16 to 15 percent in white women.
Read the full article here.

Mar 19, 2019
Author: Cornelius J Johnson
When you’re battling depression it’s difficult not to just let the pills do the work and hope for the best. As any good mental health professional will tell you, combating the symptoms of depression can take some self-governance and work. But when our mind is working against us at these times, where do we focus our attention?
Here are five simple areas to focus on in order to reduce the impact of depression.
Sleep
When suffering from depressive thought patterns, sometimes we are prone to staying in bed for as long as possible. We take ourselves out of the equation and enjoy the warmth and comfort of the bed. But that doesn’t necessarily mean we get good rest. Often it means lying in bed worrying or thinking about things we cannot control.
“We should try view our bed as a vehicle for sleep, rather than a retreat from the world,” writes William Cosgrove, an author at Researchpapersuk and LastMinuteWriting. “It’s important that we foster a routine for ourselves of going to bed at a reasonable hour, and waking up having had a good nights sleep.”
Eat
Depression can have varied effects on how we use or view food. For some, the thought of eating can make us nauseous, and for others, we seem unable to get enough. When going through depressive periods we may either eat one particular kind of food or binge on snacks and junk food.
This fluctuation in our diets can have radical effects on our state of mind. The more we randomize our intake of nutrients the more likely it is that we’ll find ourselves in a bad place. Regular, healthy eating is vital to a good state of mind. If you face depression, keep motivated to maintain a strong routine of eating healthy food.
Exercise
If you’re suffering from depression, the last thing you want to do is go out to the gym. Depression can be linked to body image or how we interact socially. As the gym combines both of these elements, it is understandable that those who suffer from depression aren’t likely to hit the gym any time soon. But this doesn’t mean you should abandon exercise totally.
Exercise is a great way of releasing endorphins. Many who suffer from depression take up solo activities, such as long distance running, walking or cycling. These activities offer us an opportunity to zone our minds on the simple act of physical movement rather than the abstract thoughts that come with depression.
Socialize
Depression is a lonely state of being, and it can be tempting to fuel that loneliness by refusing to inflict on others. We get caught up with the notion that we are no fun to be around when we are depressed. It’s important to remember that our good friends are able to support us at these times.
As a society, people are becoming more open and honest about mental health, and those who suffer from depression should no longer feel they have to be secretive about it. Explain to your close circle the issue you are facing and you’ll soon find that you have allies to help you fight your corner.
Express yourself
“History is full of people who have turned depression to their advantage,” says Miranda Rhodes, a regular contributor to Draftbeyond and Writinity. “20th-century writers were often prone to depressive or anxious states. Though you need not expect yourself to write ‘A Farewell to Arms’ or ‘The Bell Jar’, writing or painting are excellent ways of channeling your depression into something beautiful.“
In getting our depression out into something we can read or view, we are able to objectify it and analyze it without being too close to it.
Cornelius J Johnson specializes in marketing and different aspects of entrepreneurship. He writes on a variety of subjects such as finance and marketing as well as lifestyle and personal development and is a regular contributor to Lucky Assignments and Gum Essays, academic writing websites.

Mar 18, 2019
First published on ScienceDaily.com
The choices we make every day can have a lasting effect on our heart and vascular health. Adopting a heart healthy eating plan, getting more exercise, avoiding tobacco and managing known risk factors are among the key recommendations in the 2019 Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease guideline from the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA). Also, it is recommended that aspirin should only rarely be used to help prevent heart attacks and stroke in people without known cardiovascular disease.
The guideline, presented today at ACC’s 68th Annual Scientific Session, offers comprehensive but practical recommendations for preventing cardiovascular disease, which remains the leading cause of death for both men and women in the United States. Nearly 1 out of 3 deaths in the U.S. is due to cardiovascular disease.
“The most important way to prevent cardiovascular disease, whether it’s a build-up of plaque in the arteries, heart attack, stroke, heart failure or issues with how the heart contracts and pumps blood to the rest of the body, is by adopting heart healthy habits and to do so over one’s lifetime,” said Roger S. Blumenthal, MD, co-chair of the 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease and the Kenneth Jay Pollin Professor of Cardiology at Johns Hopkins Medicine. “More than 80 percent of all cardiovascular events are preventable through lifestyle changes, yet we often fall short in terms of implementing these strategies and controlling other risk factors.”
Read the full article here.

Mar 15, 2019
This text was was first published on www.svds-at-target.eu
In November 2018 the Zoom@SVDs study included the 60th participant, thereby reaching its milestone for midterm recruitment. The Zoom@SVDs study is an observational study that aims to advance our understanding of Small Vessel Disease, a condition in which the small blood vessels in the brain are damaged. We do this by zooming in on the small vessels with one of the strongest MRI scanners currently available for humans, located in the UMC Utrecht.
This study builds on a collaboration between the LMU in Munich (Germany) and the UMC Utrecht (Netherlands). In order to undergo a scan in the strong MRI in Utrecht, the 28 participants that were recruited so far in Munich travelled from all over Germany to Utrecht for an additional visit. Of course, the logistics of this study are very challenging, because flight tickets, train tickets and hotels have to be arranged as well. Also, all study information needed to be officially translated from Dutch to German and the researchers in Utrecht had to refresh their German language skills. However, these joined efforts have resulted in fast recruitment with happy participants and high-quality data.
Analyses of the first patient data have just started, of which we aim to publish the first results in the coming year. Of course, we will continue our recruitment and will continue to work in close collaboration. This study builds on our dedicated participants and good teamwork; thanks to all involved!
Mar 12, 2019
First published on ScienceDaily.com
Tumult in the bacterial community that occupies your gut — known as your microbiome — doesn’t just cause indigestion. For people recovering from a stroke, it may influence how they get better.
A recent study by Allison Brichacek and Candice Brown, researchers in the West Virginia University School of Medicine, suggests that stroke patients’ microbiomes — and even the structure of their guts — may still be out of kilter a month after the stroke has passed.
“We’re interested in the gut-brain axis — how the gut influences the brain and vice versa,” said Brichacek, a doctoral student in the immunology and microbial pathogenesis graduate program. She presented her findings at the International Stroke Conference in February.
Previous studies indicated the immediate effects a stroke can have on someone’s microbiome, but they didn’t explore whether these effects lingered. To find out, Brichacek, Brown and their colleagues — including Sophia Kenney, an undergraduate majoring in immunology and medical microbiology, and Stan Benkovic, a researcher in Brown’s lab — induced a stroke in animal models. Other models — the control group — didn’t have a stroke. The researchers compared the two groups’ microbiomes three days, 14 days and 28 days post-stroke. They also scrutinized their intestines for microscopic disparities.
Bacterial friend or foe?
One of the researchers’ discoveries was that a certain family of bacteria — Bifidobacteriaceae — was less prominent in post-stroke models than in healthy ones both 14 and 28 days out. If the name of the family sounds familiar, that’s probably because Bifidobacterium — a genus within the Bifidobacteriaceae family — is a common ingredient in yogurt and probiotics. These bacteria are known for supporting digestive health and may be associated with better outcomes in stroke patients.
Read the full article here.






 In 2018, SAFE and ESO released the “Stoke Action Plan for Europe 2018-2030”, which proposes a holistic approach to stroke management, from prevention to acute care, rehabilitation and life after stroke. The report sets out minimum targets to be reached by every European country, to equilibrate the quality of care across Europe.
In 2018, SAFE and ESO released the “Stoke Action Plan for Europe 2018-2030”, which proposes a holistic approach to stroke management, from prevention to acute care, rehabilitation and life after stroke. The report sets out minimum targets to be reached by every European country, to equilibrate the quality of care across Europe.











