Jul 30, 2018
Brussels, July 30, 2018- The eLearning Module 3 of the Stroke Support Organisation Faculty Tool (SSOFT) is published today at the following address www.ssoft.info.
SSOFT’s third module focuses on understanding different types of evidence; how to collate it and how Stroke Support Organisations can use it to their advantage:
3.1 – Use of evidence
3.2 – Types of evidence
3.3 – Interpreting evidence & data
3.4 – How SSOs generate data & evidence
3.5 – Using evidence & data in your communications
Stroke Support Organisations have been at the heart of this tool. For newer or smaller organisations, the information in the tool will provide knowledge that will help them to build and grow their communities.
Larger organisations can also benefit from SSOFT, which can enable them to support their communities and other stroke professionals across Europe, adding more voices to their movement/arguments for change.
This tool is also for anyone who is interested in knowing more about what an SSO is, how to start and develop one and how to make it sustainable.
For those interested in using this innovative eLearning platform, we would encourage them to visit the SSOFT website www.ssoft.info
About SSOFT
SSOFT is an innovative online eLearning advocacy tool being developed by Stroke Alliance for Europe (SAFE), in partnership with the European Stroke Organisation (ESO).
This online learning platform provides knowledge and training on how the creation of effective advocacy activities and campaigns to deliver positive change at a local and national level on stroke prevention, treatment and care. The eLearning platform will include six modules that provide information on:
Module 1: Stroke Support Organisations (SSOs)
Module 2: Making Change Happen
Module 3: Use of Evidence
Module 4: Role of Patient Voice
Module 5: Health System Advocacy
Module 6: Public Advocacy
The modules and learning environment is accessible via the SSOFT website through a simple registration process. Visitors to the website can also learn more about SSOFT, SAFE and ESO, find their nearest SAFE Stroke Support Organisation (SSO) as well as hear from SAFE members about their experiences.
For more information, please send an email ssoft@safestroke.eu or visit www.ssoft.info
Acknowledgments
SAFE would like to take this opportunity to thank and acknowledge the contributions made by those who have helped in the development of SSOFT and module 1.
Stroke Alliance for Europe Board, who have been involved at every stage of development of this module.
The Peer Reviewers for module 3:
- Stiftung Deutsche Schlaganfall-Hilfe (Dr Markus Wagner)
- Hellenic Alliance/Action for Stroke Support Organization (Dr Hariklia Proios)
- Macedonian Stroke Association (Dr Anita Arsovska & Dr. Maja Bozinovska Smiceska)
- Norsk forening for slagrammede (Ms Grethe Lunde)
- Thessaloniki and Wiesbaden NRZ, Rehabilitation Center Germany (Dr Dimitris Artemis)
- Aristotle University, Greece (Dr Katerina Nicolaidis)
- Anagenissis Rehabilitation Center, Greece (Ms Eugenia Stamatiou)
Our members who have shared their experiences and knowledge in the video interviews used within the module:
- Chris Macey – The Irish Heart Foundation, R.Ireland
- Pnina Rosenzweig – Neeman Association for Stroke Survivors, Israel
- Ove Puisto – STROKE-Riksförbundet, Sweden
- Markus Wagner – Stiftung Deutsche Schlaganfall-Hilfe, Germany
- Monique Lindhout – Hersenletsel, Netherlands
Our partner organisations who have collaborated in the development of the module content:
- World Stroke Organization
- European Stroke Organisation.
And all those who participated in the User Acceptance Testing of Module 3.
We would also like to thank the project sponsor Bayer Healthcare who have supported this project through an education grant.
About SAFE
The Stroke Alliance for Europe (SAFE) a non-profit-making organisation formed in 2004. It is the voice of stroke patients in Europe, representing a range of patient groups from 30 European countries.
SAFE’s goal is to decrease the number of strokes in Europe by advocating for better prevention, access to adequate treatment, post-stroke care and rehabilitation.
For more information about SAFE, please visit www.safestroke.eu

Jul 27, 2018
The 15 min round table discussion by Christina Sjöstrand, Stockholm, Hans-Christoph Diener, Essen and George Ntaios, Thessaly, focuses on the concepts of randomized clinical trials for secondary stroke prevention in patients with embolic stroke of undetermined source (ESUS). Two large clinical trials tested the hypothesis that non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants (NOACs) might be superior to aspirin in preventing recurrent strokes after ESUS.
ESUS is a type of ischemic stroke with unknown origin, i.e. for which no probable cause can be identified after standard diagnostic evaluation. Thus, ESUS is a subgroup of cryptogenic stroke, which also includes strokes with incomplete evaluation and those for which more than one probable cause. Non-lacunar strokes in patients without no major-risk cardioembolic source (such as atrial fibrillation), no major atherosclerosis of the arteries supplying the brain infarct area and no other specific cause of their stroke are identified as ESUS.
Current strategy for secondary stroke prevention is based on antiplatelets but stroke recurrent rates remain high. A historical trial, WARSS, pointed at a potential advantage of anticoagulation over antiplatelet in patients with cryptogenic stroke. There is broad evidence for anticoagulation for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation, thus providing another rationale for testing anticoagulation in ESUS.
Two large trials randomized ESUS patients for long-term treatment with either a NOAC or aspirin: NAVIGATE ESUS was stopped after an interim analysis as efficacy was not different with rivaroxaban compared with aspirin but showed an increased risk of major bleeding. RE-SPECT ESUS is still ongoing as planned; in this trial dabigatran is tested against aspirin. Results will be presented in October 2018. If the trial is positive, i.e. showing greater efficacy of dabigatran in the prevention of stroke recurrence than aspirin, this may not only have great implications of how ESUS patients are treated but could also lead to a simplified post-stroke diagnostic workup for most patients with ischemic stroke.
Please click on the photo below to access the round table video.

Jul 25, 2018
Every year, up to 1.3 million people in Europe suffer a first stroke. Acute stroke treatment strategies such as acute treatment of patients in a stroke unit, intravenous thrombolysis and endovascular treatment significantly improve the outcome for patients with ischaemic stroke and thus reduce its socioeconomic burden. However, reliable data on access to and delivery of acute stroke treatment strategies throughout Europe are lacking.
The European Stroke Organisation (ESO), the European Society of Minimally Invasive Neurological Therapy (ESMINT), the European Academy of Neurology (EAN) and the patient organisation Stroke Alliance for Europe (SAFE) have therefore surveyed stroke experts from 44 of 51 European countries on the best available information regarding national access to and delivery rates of acute stroke unit care, intravenous thrombolysis, and endovascular treatment.
The results of this survey identify major inequalities in acute stroke treatment, with many countries reporting rates that were far below highest country rates. This article shows in which countries patients still have no or obviously inadequate access to appropriate acute stroke treatment.
According to Urs Fischer, Professor for Acute Neurology and Stroke at the University Hospital Bern, up to 226,662 additional patients could be treated with intravenous thrombolysis and an additional 67,347 with endovascular treatment each year. “Many stroke victims in Europe still have no access to acute stroke treatment,” he said. “If stroke unit care, intravenous thrombolysis and endovascular therapy would be routine practice throughout Europe, many more victims could survive their stroke without a major handicap”. According to Prof. Fischer, these inequalities not only have a major impact on the patients, but also on their families and the socioeconomic burden. “Recent studies have shown, that acute stroke treatment is highly cost effective – if you treat your patients right, you will not only improve the quality of life of the patient and his family, you will also save money for your society”, he said. Therefore, efforts have to be done to increase the number of stroke units, intravenous thrombolysis and endovascular stroke therapy. “We have to talk to governments, politicians, health care specialists and stroke physicians in order to set up and improve the system in regions, where acute stroke treatment is lacking!”
In May 2018, ESO and SAFE presented the Stroke Action Plan for Europe to set achievement goals for stroke care by 2030. This survey already provided important insights for the Stroke Action Plan authors. The findings from this survey are relevant for future health-care planning in Europe and beyond.
Contact
Prof. Dr. med Urs Fischer
Department of Neurology, University Hospital Bern
urs.fischer@insel.ch European Stroke Organisation www.eso-stroke.org
Article Title and Citation
Access to and delivery of acute ischaemic stroke treatments: a survey of national scientific societies and stroke experts in 44 European countries
http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/2396987318786023
Authors
Diana Aguiar de Sousa, Rascha von Martial, Sònia Abilleira, Thomas Gattringer, Adam Kobayashi, Miquel Gallofré, Franz Fazekas, Istvan Szikora, Valery Feigin, Valeria Caso, Urs Fischer, on behalf of the ESO ESMINT EAN SAFE Survey on Stroke Care collaborators
About the Authors
Diana Aguiar de Sousa: First author
Diana Aguiar de Sousa is Neurologist at Hospital de Santa Maria, in Lisbon, and assistant professor of Neuroanatomy at University of Lisbon. She is clinical investigator at Instituto de Medicina Molecular and PhD student at University of Lisbon, under the guidance of Prof. JM Ferro and Prof. P. Canhão. She completed the Clinical Scholars Research Training Certificate Program from Harvard Medical School and a European Academy of Neurology Research Fellowship in acute stroke at Inselspital Bern, Switzerland. Diana Sousa was awarded with the European Stroke Organization (ESO) Young Investigator Award in 2016. She is member of the ESO Young Stroke Physicians and Researchers Committee.
Urs Fischer: Corresponding author
Urs Fischer (urs.fischer@insel.ch)is Professor for Acute Neurology and Stroke (Extraordinarius) at the University Hospital (Inselspital), Bern. He is chair of the Neurological Inpatient Department, co-chair of the Stroke Center Bern, and deputy director of the Clinical Trial Unit (CTU) of the University of Bern. He is a clinical researcher and his main research interest involves diagnosis, treatment and outcome of patients with acute neurological diseases. He is co-principal investigator of the SWITCH study (www.switch-trial.ch), principal investigator of the ELAN trial (www.elan-trial.ch) and co-principal investigator of the SWIFT DIRECT trial (www.swift-direct.ch). Urs Fischer is Secretary General of the European Stroke Organisation (ESO), treasurer of the Swiss Neurological Society (SNG) and co-founder the ESO ESMINT ESNR Stroke Winter School, which is regularly held at the University Hospital in Bern, Switzerland.

Jul 24, 2018
Since this May, in selected hospitals in 12 European countries: Spain, Serbia, Poland, Czech Republic, Latvia, Croatia, Macedonia, Greece, Ukraine, Georgia, Hungary and Turkey, stroke patients and their carers are being provided with information on stroke and important next steps on their path to recovery.
The patient-focused materials are made of five brochures, including a list of national, regional and local stroke support organisations, with their contact details, in order that patients and carers can access further support in the months and years following their stroke. The information provided in the brochures are kindly provided by the Stroke Association UK and then translated to all project languages, applying the information standard procedure for the translation.
The next step in SAFE Angels project consists of collecting feedback from patients and their carers about the quantity and quality of information they have been provided with during their stay at the hospital, before being discharged. The feedback will be collected through an online survey in all 13 project languages (Spanish, Catalan, Serbian, Polish, Czech, Latvian, Croatian, Macedonian, Greek, Ukrainian, Georgian, Hungarian and Turkish).
Please see the survey on this link and inform the people you know.
For more information about the hospitals which are providing patient materials, please find an organisation which is working in your country here.
If you are interested in finding out more about the SAFE Angels project, please contact Jelena Misita, SAFE Awareness and Advocacy Manager at jelena.misita@safestroke.eu.
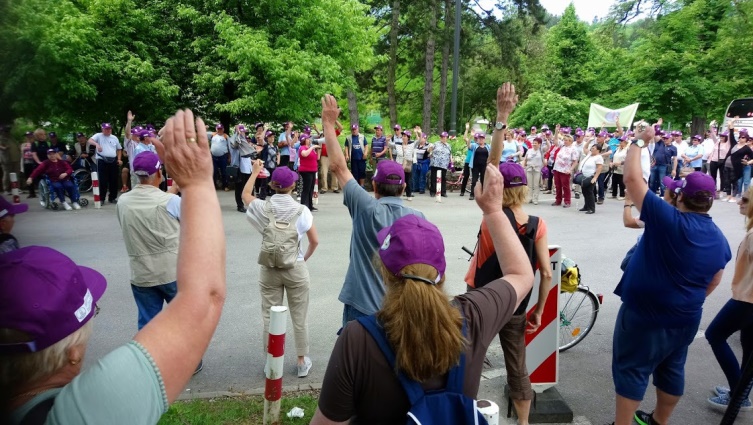
Jul 23, 2018
Slovenian stroke support organisation »Združenje bolnikov s cerebrovaskularno boleznijo Slovenije« is one of SAFE’s very active members. We recently received an authored text about their stroke awareness activities in May 2018 from Jelka Janša, who is an active member of the Slovenian stroke support organisation and past SAFE President.
…
Written by Jelka Janša
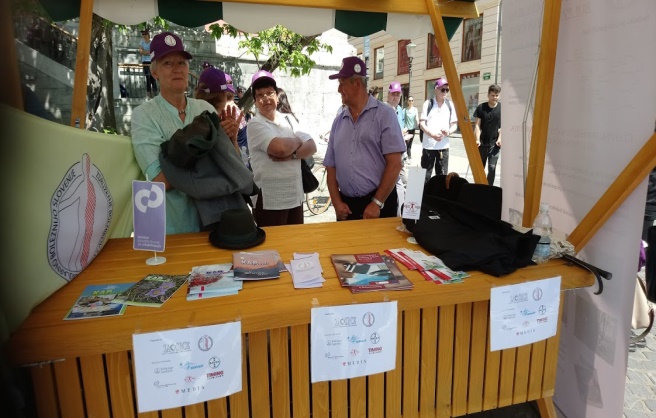
 To promote the European Stroke day, there were two main activities namely: the city walk in Ljubljana and two teleconferences. In addition, 400 posters with message about FAST campaign in Slovenian – GROM were displayed around Slovenia for a period of April 24 till May 8. Further to that, 8 professional lectures were sponsored to be delivered within stroke clubs around Slovenia aiming to share again information about the facts about stroke.
To promote the European Stroke day, there were two main activities namely: the city walk in Ljubljana and two teleconferences. In addition, 400 posters with message about FAST campaign in Slovenian – GROM were displayed around Slovenia for a period of April 24 till May 8. Further to that, 8 professional lectures were sponsored to be delivered within stroke clubs around Slovenia aiming to share again information about the facts about stroke.
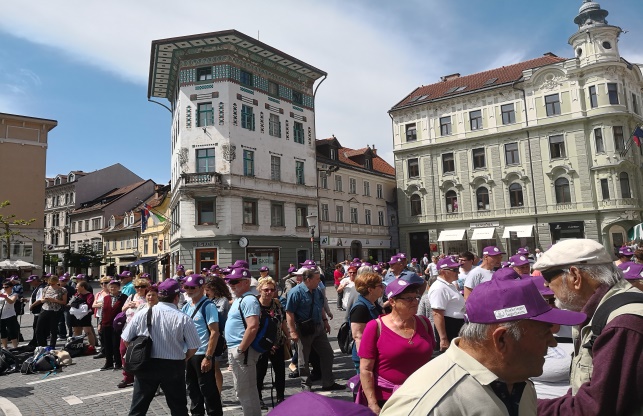
 Second city walk in Ljubljana was on actual European Stroke Day, May 8. This year the distance was 1,6 km and there were 260 stroke survivors and their supporters attending. It ended at the city Centre, »Prešernov trg«, were there were stands with information about stroke, its prevention including leaflets about Slovenian Stroke Support Organisation and Slovenian Heart Organisation. People, passing by, had the opportunity to have their cholesterol and blood pressure checked. There were four speeches, by Milan Čuček, president of SSSO, Tatjana Erjavec, vice-president of the SSSO, Mr. Zalar from Heart organisation and by Mr Jankovič, the major of Ljubljana. Participants continued with a lunch at the Livada restaurant in Ljubljana.
Second city walk in Ljubljana was on actual European Stroke Day, May 8. This year the distance was 1,6 km and there were 260 stroke survivors and their supporters attending. It ended at the city Centre, »Prešernov trg«, were there were stands with information about stroke, its prevention including leaflets about Slovenian Stroke Support Organisation and Slovenian Heart Organisation. People, passing by, had the opportunity to have their cholesterol and blood pressure checked. There were four speeches, by Milan Čuček, president of SSSO, Tatjana Erjavec, vice-president of the SSSO, Mr. Zalar from Heart organisation and by Mr Jankovič, the major of Ljubljana. Participants continued with a lunch at the Livada restaurant in Ljubljana.
Two teleconferences were held to emphasize the message about Life after stroke and stroke facts; the first one already on April 23 and organized by Slovenian Heart organisation with representatives from SSSO. They were talking about stroke issues and notified the journalist already about the ESD and the next teleconference, on May 23. The May’s conference was organized by the SSSO and in addition to talking about the life after stroke issues, Tatjana Erjavec also spoke about »Stroke Action Plan in Europe«, the policy paper prepared by both the SAFE and ESO and presented at the same day in EP.
May activities have been well covered by national and local media with 66 publications, including TV, radio and newspapers.The activities were kindly sponsored by University rehabilitation Institute –SOČA, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medis, Soča Oprema, Timing Ljubljana, SERVIER Pharma and Mountain Rescue team.
Please look at some of the photos from these activities.






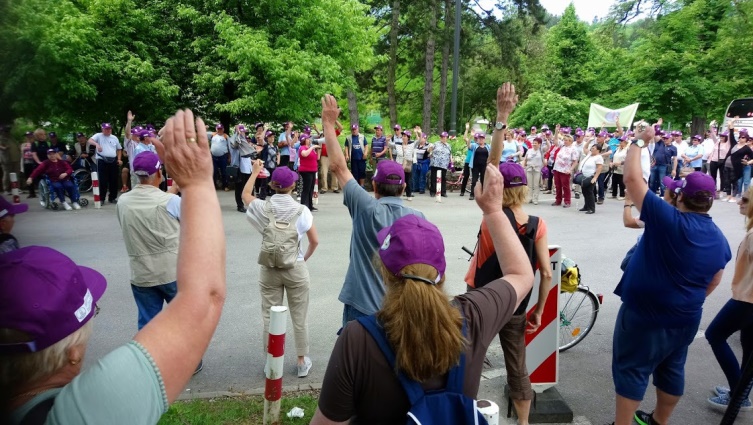

Jul 20, 2018
The World Stroke Congress 2018’s late breaking abstract submission is now open. Don’t miss this last opportunity to be part of this year’s program! Share your work now, and get valuable feedback from colleagues and leaders in the field, opportunities for collaborations and ideas for future research. Review the topics and the guidelines, and submit your abstract today.
The deadline for submission is August 15. Find all the information here.


Jul 17, 2018
According the Turkish Statistical Organisation, one person dies every 14 minutes because of stroke in Turkey and 40.000 people died of stroke in 2017.
As much as these data seem horrifying, there is a hope for change. Since recently, there is a stroke support organisation in Turkey, dedicated to raising awareness and helping stroke survivors and their families. The organisation is called BEYINDER and since December 2017 it is a full member of SAFE. We used the opportunity to ask some questions to the Board of this organisation, made of medical experts whose enthusiasm led to forming the patient support organisation and joining SAFE. Below are the answers sent to us by Prof. Derya Uluduz from Istanbul University, Cerrahpasa School of Medicine, on behalf of the whole Board of the BEYINDER organisation.
1. How and when was your organisation BEYINDER formed?
In November 2015, we participated one of the SAFE meetings on behalf of Turkish Neurological Society and we were very impressed about what SAFE trying to do. In fact, as Turkish stroke neurologists we were doing many acitivities but all were based on individual efforts. In this meeting we had the feeling that we need to have a patient society to influence and extend to all country and we should be a member of SAFE organisation. SAFE was doing enormous work and we needed to be part of this. People in SAFE were so friendly, they encouraged us for this and tried to explain the process step by step. Especially I should thank to dear Sarah Belson, Marina Charalambous, Pnina Rosenzweig and Anita Arsovska. I appreciate them for their encouragement and motivation. We first tried to form the organisation under the auspices of Turkish stroke society but the problem was one third of the board should be made up from stroke survivors, so this could not be done. We need to form a separate non-profit organisation. We tried to find patients who can participate to this organisation and one of our board member suggested to provide us an Office place for the organisation. Another board member who was our patient was a certified public accountant who knows the paperworks for registration process. We provided a sample constitution form from Sarah Belson to arrange ours and at the end BEYINDER was formed in August 2017.
2. Are you covering with your activities the whole country or some specific regions?
We are covering the whole country. We are in contact with all stroke centers in order to reach more stroke patients. The main office of the society is in Istanbul. Our future plan is to open branch offices in some other cities. Also we want to include family physicians in primary care to our organisation and collaborate with them.
3. What is the situation with stroke in Turkey, how many new strokes do you have per year and is the level of treatment at a satisfactory level, in your opinion?
Even the epidemiological studies are limited in Turkey, the incidence of stroke is high and it is increasing even in young population. The incidence for ischemic stroke was about 119/100.000 in 1990 and was 134/100.000 in 2010, for hemorrhagic stroke it was 32/100.000 in 1990, and 43/100.000 in 2010. Although mortality rate is decreasing over the decades, stroke is still the second leading cause of death in our country. According the Turkish Statistical Organisation, one person died every 14 minutes because of stroke in Turkey and 40.000 people died with stroke in 2017.
The population does not have enough knowledge and are not aware of the acute stroke treatment and primary/secondary prevention. But the good news is that for 2 years Turkish Ministry of Health and Social Security institution have started to work hard to enhance the acute stroke treatment strategies and facilities in all over Turkey. For primary prevention, public service announcements on television and billboards around country advice people to stop smoking, control blood pressure and increasing physical activity. But we still dont have enough well organised stroke centers for acute treatment and transportation systems are still big problem in big cities for early management in stroke. Neurorehabilitation facilites are generally limited to big cities mainly due to lack of facilities and qualified person in stroke rehabilitation. In big cities stroke survivors can get benefit from the govermental rehabilitation centers or physical therapists are able to visit patients at their homes if necessary. We need to increase the awareness of primary and secondary prevention in stroke and force the goverment to increase the facilities and qualified person in stroke. Another problem is mainly physicians hesitate to prescribe anticoagulation due to side effects in patients with atrial fibrillation leading to stroke.
4. How is your organisation engaged in raising awareness of stroke and what are you preparing for the World Stroke Day, on 29th October this year?
After being a member of SAFE organisation we have continued our attempts for the awareness of stroke under the umbrella of SAFE. First we translated and prepared the posters about the risk factors of stroke and hanged them on the most seen places of clinics and outpatient clinics of neurology at several hospitals around the country. By this way, the patients admitted with any neurological complaints as well as the stroke survivors and their relatives had been able to learn the risk factors of stroke which is important for the primary and secondary prevention.
We have begun to publish a free public magazine quarterly named BEYİNDER which concerns with all about stroke, current knowledge of risk factors and important points about stroke, healthy diet, physical exercise, ways to increase quality of life after stroke, and etc.
On World Stroke Day some of our board members attended TV programs about stroke. On the 2018 European Stroke Awareness day we held an organisation in a big research hospital inviting the stroke survivors and their relatives. A stroke neurologist gave a talk about the risk factors, primary and secondary prevention. A physical therapist demonstrated some exercises for rehabilitation. In the social programme, after the lunch we went to the garden of the hospital and flied many colourful balloons to the sky.
5. What are the future short term plans for BEYİNDER?
– We will revise our website including the list of all stroke neurologists in Turkey, so stroke survivors will be able to reach a stroke specialist close by. People will have chance to ask questions through website contact area and get the answers from the experts.
– Patient education school for stroke survivors and public will be held twice a year. Each will be at different hospitals with different topics of stroke.
– In September, we are going to hold a garage sale and planning to sell new and vintage clothes, furniture and different kind of donated objects together with some of our patients. Our quarterly public magazine will be still published.
– If we can solve the financial part, one of our aim is to hold the first national stroke. We are not sure if we can manage this in the World stroke day period but, the congress will be without any charge and approximately 100 stroke survivors and one relative will be invited. During 2.5 days experts will give educations for primary prevention and secondary care, rehabilitation, cognition and increasing quality of life and their relatives how to combat with patients problems after stroke.
– On the World Stroke Day, on 29th October, we are planning to visit some schools to engage and educate the pupils on stroke in an enjoyable way. Also we plan to do visit the Ministry of Health and talk about the problems and needs of stroke survivors in Turkey. In one of our hospitals we will have a party for stroke day, increasing the awareness, we will invite stroke survivors and organize an arbor day in selected area in the hospital garden.
6. This year’s topic for the World Stroke Campaign is Life After Stroke. How would you describe the quality of life after stroke for people in Turkey?
Stroke rehabilitation and long term care became more important with the recent advances in stroke patients. One of the most difficult aspect of having a stroke is the adapting to life for both the patients and caregivers. Comprehensive stroke units provides multidisciplinary team approaches for acute treatment and rehabilitation for stroke patients. Although the number of dedicated stroke centers has been increasing in last years, there are still some regions without stroke centers in Turkey. In Turkey even the importance is known, rehabilitation program after stroke is mainly bounded by physical motor rehabilitation that is probably due to lack of qualified therapists specialized in speech therapy, swallowing therapy, occupational therapy and psychological therapy. Unfortunately, a very small number of centers in Turkey can provide such comprehensive therapies. Nevertheless, government is making efforts to educate and establish stroke rehabilitation team in recent years.
There is also lack of awareness about the importance of assessment of quality of life in stroke patients. Measurement of quality of life is not routinely used in many centers in Turkey. We also do not have enough time for assessing the quality of life in outpatient clinics due to high number of patients we should examine daily.
There is a lack of public awareness about the importance of rehabilitation after stroke. We are planning educational campaigns in order to increase public awareness about the importance of rehabilitation after stroke. Furthermore we should try to force the government to educate specialists and to increase the number of household stroke care system like home care service, transport of patients to the rehabilitation facilities. Also general health insurance covers a short term period of rehabilitation, that should be extended.
Our aim is to communicate with the government in order to increase the number of rehabilitation facilities and also most importantly specific rehabilitation centers for stroke patients. Turkish Ministry of Health provides home care service for only bedridden patients and in place health service for those who live in places such as rest home, prison or nursery. Also family physicians coordinate the home care services. Patient’s all health conditions are assessed and physicians decide the need for home care service. Then follow-up and treatment plans are made according to the result of assessment.
Although there are services that ensures medical care and rehabilitation for stroke patients, family members in the home environment are also very important for everyday living of stroke patients for whole life. According to the the family structure in Turkey, most people think that the care of patients and elderly people is under the responsibility of the family members. Because of this cultural customs relatives think this is a duty and caregivers in Turkey have many psychological comorbidities during patient care. Caregivers have many responsibilities such as physical rehabilitation help, feeding, hygienic care etc. In Turkey we don’t have day care facilities or long term inpatient hospitals for those people. There should be psychological support as well as social support for caregivers to increase their awareness about the importance of their role, reduce burden of care. One of the priority aims of BEYİNDER is to establish appropriate social support systems for the caregivers.
Physical conditions are not well established for disabled people in Turkey, but recently there is increasing awareness about the functional needs for daily living of disabled patients in the community forcing the goverment.
7. Your organisation is a full member of SAFE since December 2017. What made you join SAFE and do you consider it’s useful for organisation to cluster this way?
We perceived that there is a huge need for this kind of organisation in our country. We formed BEYINDER to help stroke survivors and to increase awareness of stroke in the community, we planned to be a part of an international organisation. Fortunately we became a full member of SAFE at December 2017. SAFE is an organisation aimed to driven-up stroke at European political agenda and to educate population about stroke primary and secondary prevention.
It was important for us to provide standardization of our organisation and become widespread to all country. Working together with SAFE like a team facilitate to accomplish the projects and more voices more ideas increase our awareness and perspective as well. SAFE works enormously, helps the organisations without any egocentrically without insisting just suggesting. This makes us feel good and work harder and harder for SAFE. SAFE is like a best teacher and we are trying to work hard and to do our best to get praise. SAFE is motivating us much. And also to learn more from an international organisation will increase our knowledge.

Jul 17, 2018
Having a stroke is a terrifying experience, and it is only natural to start experiencing some symptoms of anxiety and depression when it is all over. After all, it is something that often brings a person close to death, and it can seem like no one else understands the feelings of fear and despair that often accompany survival. While you often feel thankful that you were able to make it through, there is nothing wrong with the negative feelings that come with it. Here is how your canine companion can help you get through this tough phase after a stroke.
Alleviating Anxiety and Depression
These are natural things to feel after a stroke, but a dog can help you get through them. Petting and hugging them releases oxytocin throughout the body, and this is the hormone responsible for reducing anxiety and stress, blood pressure, and heart rate, so you feel more relaxed and a lot less worried. They also bring comfort as a whole because you know they are always there when you need them.
They give you a sense of purpose and validation, as well as offering unconditional love that cannot be matched by another creature on this planet. There have even been studies to suggest that they are able to help the process of balancing the serotonin levels in your brain, boosting your mood and leaving you feeling in a better mindset.
Reducing Feelings of Loneliness
Often, post-stroke life can leave a person feeling increasingly lonely, and this can happen for a number of reasons. Sometimes, a lot of attention will have been received in the hospital, and family will have made special arrangements to come visit and be there as much as possible.
However, once everything is clear, life goes back to normal, and it can leave a person feeling isolated. A dog is always there to offer love, support, and companionship, and this can bring a great deal of comfort, as well as reduce feelings of loneliness and isolation.
Giving You Someone to Talk to
Possibly the most important thing that a dog can do for you is give you someone to talk to when you need it most. They will not judge or abandon you, regardless of how emotional you are. A shoulder to cry on, there is nothing you cannot tell them – especially as they will never tell anyone else. Linking to the fact that they can help with loneliness, it is important to have someone to speak to in these circumstances, and sometimes another human is not the easiest or best choice for you. A dog can offer just as much, and more.
To Conclude
If you found this interesting and would like to learn more about the ways in which a dog can help with mental health, feel free to check out this detailed resource. Dogs are some of the greatest companions we could ever ask for, and as little as we give them, they always return it tenfold. We understand the struggle that comes after a stroke, and your dog is there to help you through the darkest moments in every way they can.
About the Author

Will Tottle
Will Tottle is a freelance writer, his blog can be seen here . If you are interested in more information on the benefits of dog ownership including health tips, buyer’s guides and gear reviews, then check out his guides over at Dogowner.co.uk
Follow on Facebook or Twitter

Jul 2, 2018
Research project led by the UKE: Clinical Trial in eight European countries has started
When stroke is treated by thrombectomy, blood clots are removed from the arteries of the brain with the help of a catheter in order to rebuild the blood circulation in the damaged area. So far, this therapy is only used regularly in specialized centres if the stroke had not already casued significant damage to the brain.
The research project TENSION, under the leadership of researchers of the Universitätsklinikum Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE), will show whether patients affected by a severe stroke with already extended brain damage can also benefit from this treatment. In close collaboration with the Universitätsklinikum Heidelberg, the study has now started at 40 locations in eight countries. The project is funded by the European Union with a 6 million Euro grant.
Most strokes are caused by a blood clot (thrombus) which blocks a blood vessel in the brain so that parts of the brain can no longer be supplied with oxygen. The longer the vascular obliteration continues, the more brain tissue dies. Blood clots obstructing large brain arteries can be removed by endovascular treatment by introduction of a catheter starting from the groin into the arteries of the brain. This treatment, which is called thombectomy, is effective and has become standard of care for patients in whom only a few brain tissues are injured. Under these circumstances, patients have very good chances to live an independent and unimpeded life after a stroke. Whether this treatment can also help patients with severe strokes with already extended brain damage is still unclear. Therefore, these patients are currently not treated with thrombectomy in routine clinical practice.
“With our research project, TENSION, we aim to prove that patients with already extended lesions can also benefit from thrombectomy”, says Prof. Dr. Götz Thomalla, project Coordinator and lead-ing senior physician in the Clinic for Neurology of the UKE. “If our assumptions are true, the trial will provide evidence for effective treatment for a large number of patients with severe stroke and already extended brain damage.“
Clinical Study: 40 study sites, 714 patients
In the clinical trial, up to 714 patients who are admitted to a hospital with a stroke in one of the 40 trial sites will be enrolled. A criterion for inclusion in the study is that brain imaging should have already shown an extended area of damaged brain tissue around the affected blood vessel. Evalu-ation of the extent of the lesion will come from imaging techniques such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance tomography. “The correct evaluation of CT and MR images by the treating physician plays a crucial role here”, says Prof. Dr. Jens Fiehler, director of the Clinic of Neuroradiology at UKE and leader of the image core lab of the TENSION study and adds: “In order to guarantee a consistently high quality of image reading in all study sites, we have developed standardized training that must be passed all physicians who participate in the trial.”
Patients are randomly divided into two groups by: Both groups will receive normal medicinal therapy, but in addition, the second group will also have the clot removed by thrombectomy. After 90 days, the stroke patient’s degree of residual disability will be ranked by means of the usual scales used in stroke treatment. “The TENSION trial will answer the most urgent clinical question concern-ing the use of thrombectomy for treatment of stroke”, says Prof. Bendszus, Head of the Department of Neuroradiology at the University Hospital Heidelberg and Coordinating Investigator of the trial. “Such an interdisciplinary effort will also help us to improve the access to this effective treatment across Europe.”
The Clinical Trial is coordinated by the Universitätsklinikum Heidelberg, while the overall research project TENSION is led by the UKE.
Contact
Prof. Dr. Götz Thomalla
Klinik und Poliklinik für Neurologie
Universitätsklinikum Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE)
Martinistr. 52
20246 Hamburg
Phone: 040 7410- 50137
thomalla@uke.de
Prof. Dr. Martin Bendszus
University Hospital of Heidelberg
Department of Neuroadiology
Im Neuenheimer Feld 400
69120 Heidelberg
Phone: +49 6221-56-7566
martin.bendszus@med.uni-heidelberg.de
Prof. Dr. Jens Fiehler
Klinik für Neuroradiologische Diagnostik und Intervention
Universitätsklinikum Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE)
Martinistr. 52
20246 Hamburg
Phone: 040 7410- 55598
fiehler@uke.de

Jun 29, 2018
Written by Anita Wiseman │ First appeared on WSO blog
After sixty-two years of officially categorizing stroke as a Disease of the Circulatory System, the newly published WHO ICD 11, has correctly classified stroke as a Disease of the Nervous System
ICD 11 is a foundation document for health policy and treatment globally and the decision on stroke classification has been warmly welcomed by the World Stroke Organisation. WSO actively advocated for the change, arguing that positioning stroke as a disease of the brain will support global efforts to increase recognition of stroke and improve access to services and treatments that save lives and reduce post-stroke disabilities. Stroke was responsible for 14m deaths and 116 DALYS in 2016 alone, directing attention to the brain and what can be done to reduce premature deaths.
To find out more about why the WSO has made it a priority to achieve this change, I talked to Bo Norrving, Chair of the organization’s Global Policy Committee. Bo has also been chair of the Cerebrovascular Diseases group for the ICD 11 and is a member of the WHO Neurology Topical Advisory Group, chaired by Raad Shakir.
Why does it really matter that stroke is classified as a brain disease, not a disease of the circulatory system – aren’t the two closely related?
It’s true that there are close links between cardiovascular disease and stroke; many risk factors are shared and primary prevention will target both disorders jointly. We work closely with colleagues in the Non-Communicable Disease (NCD) and cardiovascular (CVD) sphere to advance our common prevention agenda.
The simple fact, however, is that when strokes happen, they happen in the brain.
Delivering stroke treatment early and efficiently with effective acute therapies such as thrombolytic therapy and thrombectomy, depends on the early recognition of symptoms from the brain and early actions to call an ambulance. This is why in many countries campaigns to increase public knowledge of stroke symptoms (like the FAST campaign) have been conducted. These campaigns are founded on in recognition that ‘time is brain’. Similarly, providing early treatment of transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), which are linked to stroke and are a significant contributing factor to dementia, depends on public awareness of the symptoms and rapid admittance to hospital.
The impact of delivering effective treatment for acute stroke – and the opportunity to prevent a stroke – present huge opportunities to reduce the global burden of disease and cannot be missed if we are to are to achieve global goals on NCD reduction. Thinking beyond prevention, understanding the role of the brain in residual stroke symptoms and disabilities from stroke is critically important to providing patients with effective long-term rehabilitation and support.
Classifying stroke under diseases of the circulatory system has kept stroke in the shadows where it couldn’t easily be seen or dealt with. We are delighted that this is no longer the case and that more light can be cast to the specifics of stroke and the opportunities we have to improve prevention and treatment.
How do you think this change will help with the achievement the global goal to reduce avoidable deaths from stroke?
Stroke is the second biggest killer and the largest single cause of disability worldwide and yet still struggles to get the policy attention and resources commensurate with its global impact. Identifying stroke as a disease of the brain and pulling all types of cerebro-vascular diseases into a single block in the ICD 11 will, we believe, guide policy attention to the right place and enable us to develop 21st century services for stroke.
Stroke is probably the best example there is of a non-communicable disease that is highly preventable and highly treatable. With the right focus and commitment to stroke we can make a massive impact on the achievement of global health and development goals .






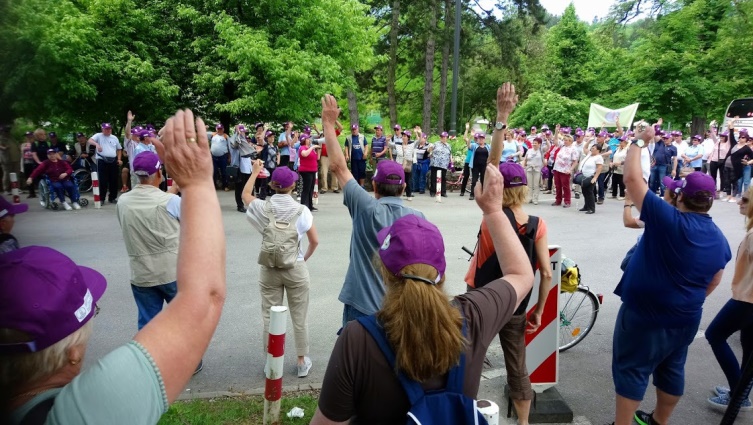
 To promote the European Stroke day, there were two main activities namely: the city walk in Ljubljana and two teleconferences. In addition, 400 posters with message about FAST campaign in Slovenian – GROM were displayed around Slovenia for a period of April 24 till May 8. Further to that, 8 professional lectures were sponsored to be delivered within stroke clubs around Slovenia aiming to share again information about the facts about stroke.
To promote the European Stroke day, there were two main activities namely: the city walk in Ljubljana and two teleconferences. In addition, 400 posters with message about FAST campaign in Slovenian – GROM were displayed around Slovenia for a period of April 24 till May 8. Further to that, 8 professional lectures were sponsored to be delivered within stroke clubs around Slovenia aiming to share again information about the facts about stroke. Second city walk in Ljubljana was on actual European Stroke Day, May 8. This year the distance was 1,6 km and there were 260 stroke survivors and their supporters attending. It ended at the city Centre, »Prešernov trg«, were there were stands with information about stroke, its prevention including leaflets about Slovenian Stroke Support Organisation and Slovenian Heart Organisation. People, passing by, had the opportunity to have their cholesterol and blood pressure checked. There were four speeches, by Milan Čuček, president of SSSO, Tatjana Erjavec, vice-president of the SSSO, Mr. Zalar from Heart organisation and by Mr Jankovič, the major of Ljubljana. Participants continued with a lunch at the Livada restaurant in Ljubljana.
Second city walk in Ljubljana was on actual European Stroke Day, May 8. This year the distance was 1,6 km and there were 260 stroke survivors and their supporters attending. It ended at the city Centre, »Prešernov trg«, were there were stands with information about stroke, its prevention including leaflets about Slovenian Stroke Support Organisation and Slovenian Heart Organisation. People, passing by, had the opportunity to have their cholesterol and blood pressure checked. There were four speeches, by Milan Čuček, president of SSSO, Tatjana Erjavec, vice-president of the SSSO, Mr. Zalar from Heart organisation and by Mr Jankovič, the major of Ljubljana. Participants continued with a lunch at the Livada restaurant in Ljubljana.















