
Apr 12, 2019
Author: Aidan Judd
In 2016 and 2017, broadcaster Mark Goodier suffered two strokes. He found when he got home from hospital, there were not that many resources to use as part of your recovery. And once you are away from constant medical supervision, it can be a lonely time as family and friends get back to their daily lives.
 Mark started the Stroke Stories podcast to seek out and hear from stroke survivors.
Mark started the Stroke Stories podcast to seek out and hear from stroke survivors.
In every episode, we hear a different stroke survivor – we hear about their condition, what inspires them, and the lessons they learned on the road to recovery.
Every stroke is different, and we reflect that in the people that we talk to for the podcast. Since November 2018, when the first episode was released, we’ve spoken to people from all different ages, backgrounds, and nationalities:
Nick and Jo Cann
Nick had a stroke when he was 50. After the stroke he found that there was a lack of support in his area for him and other stroke survivors. Despite suffering from aphasia, Nick speaks at events across the UK to raise awareness of stroke, and has also set up a support cafe meet up.
Connor and Sarah Lynnes
As a result of an injury he had whilst playing rugby, Connor had a massive stroke at just 14 years old. Connor has now set up his own foundation, to help other young survivors of stroke and brain injuries.
Clodagh Dunlop
A front-line police officer, Clodagh Dunlop was only 35 when she suffered her stroke. As a result, she experienced locked-in syndrome, which meant she was unable to move or speak. However, after 7 months of intense physiotherapy, she walked out of hospital, and is back working full time in the police force.
Antonio Iannella
Antonio suffered a stroke at the age of 38 whilst in holiday with his family in Vietnam. Since then, he has recovered well, and pursued a lifelong dream of opening and running a music recording studio in his home.
We want to spread the message as far as possible. If you are a stroke survivor and would like to feature in a future episode, then please contact SAFE, or DM us via our Twitter account – twitter.com/strokestories
Updated with new episode released every week, Stroke Stories seeks to inspire and reassure with real life stories from stroke survivors and their families.
There are currently over 20 episodes available through iTunes (https://itunes.apple.com/gb/podcast/stroke-stories/id1442493312?mt=2) and on ACast (https://play.acast.com/s/strokestories)
For the latest updates, follow Stroke Stories on Twitter – www.twitter.com/strokestories and Instagram www.instagram.com/strokestories
Apr 12, 2019
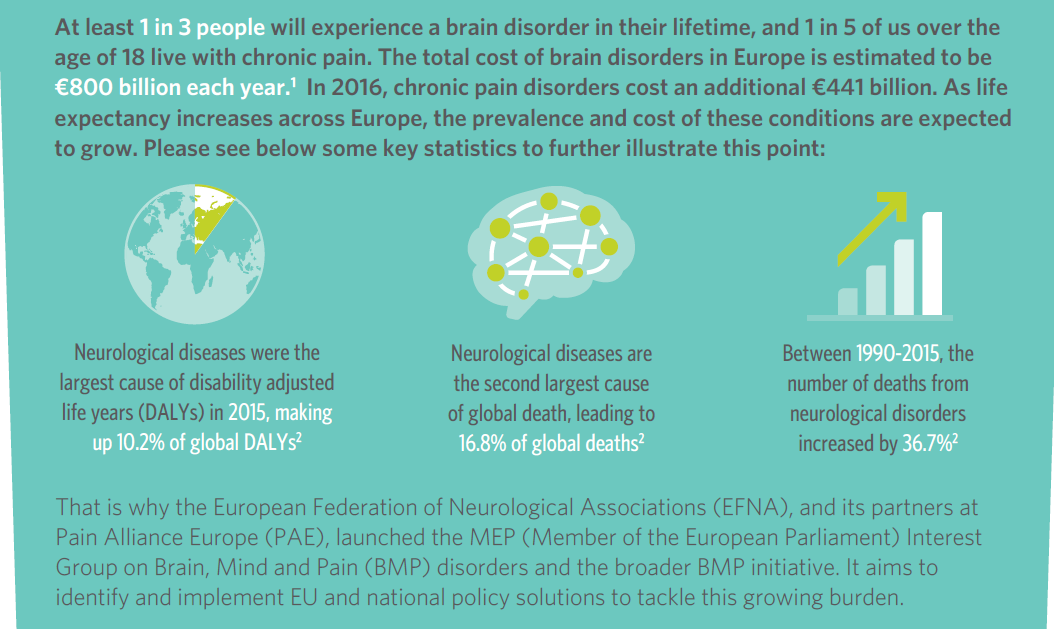
The Brain, Mind and Pain (BMP) initiative has today launched its Book of Evidence for the 2019-2024 EU mandate.
This Book of Evidence (BoE) sets a strategic vision on policy action to deliver better care for people with neurological and chronic pain disorders in the EU.
It will be used as the core policy document of the MEP Interest Group on Brain, Mind & Pain – which will continue after the upcoming EU elections for the next 5 year mandate.
The Interest Group is coordinated by European Federation of Neurological Associations (EFNA) and Pain Alliance Europe (PAE).
 The BoE outlines clear focus areas and proposes recommendations for policy actions, which, if implemented, would significantly improve quality of life for people with neurological and chronic pain disorders, as well as their families and carers.
The BoE outlines clear focus areas and proposes recommendations for policy actions, which, if implemented, would significantly improve quality of life for people with neurological and chronic pain disorders, as well as their families and carers.
The development of the document was led by EFNA and PAE and involved a wide range of key EU and national stakeholders from the patient, policy, industry and scientific communities.
This collaborative development process is reflected in wide ranging endorsements and support from organisations such as the European Commission, European Brain Council, European Patients’ Forum, European Academy of Neurology, European Pain Federation and European Alliance for Patient Access.
Key areas for action
The BoE outlines the thematic areas of focus for the MEP Interest Group on Brain, Mind and Pain for the 2019-2024 mandate. These are:
» Eradicate stigma, isolation and discrimination: A lack of public awareness of BMP disorders feeds their stigma and the associated isolation and discrimination suffered by BMP patients, carers, and their families.
» Ensure equitable access to treatment, services, and support: Access to treatment, services, and support is a topic of concern for patients in Europe due to high failure rates, delays in market access, relatively expensive treatments, and inequality in access across, but also within, EU Member States
» Promote patient empowerment for increased involvement and engagement: Patient empowerment is a means for more effective BMP patient engagement and meaningful involvement in the research, medical and policy conversations which affect them
These areas have been chosen in order to support the MEP Interest Group in leveraging current policy opportunities on the agenda whilst ensuring continuity with the past activities and successes of the BMP initiative.
Driving policy change
The 2019-2024 mandate brings with it an active policy environment at EU level, with numerous opportunities for advocacy on behalf of people with brain, mind and pain disorders.
Ensuring that the Interest Group is capable of impacting policy discussions throughout the 2019-2024 mandate will be key in making progress in the three key thematic areas identified.
Additionally, with the global priority turning more and more towards NCDs, we need to ensure that brain, mind and pain disorders are part of global health policy agenda.
To this end, each chapter of the BoE contains a section on the policy opportunities and subsequent actions that can be leveraged to further progress in each thematic area and at EU and global level.
Looking ahead
It is now the responsibility of the Interest Group and the wider BMP initiative to leverage the policy opportunities and pursue the policy actions identified in this text throughout the 2019-2024 mandate.
EFNA President, Joke Jaarsma says: ‘Progress is contingent on coordinated policy advocacy at EU and global level, taken forward by the BMP initiative as a whole and its partners.
‘Using the BoE as a springboard for action, let’s drive policy change and make a real difference to the daily lives of people living with BMP disorders across Europe!’ she continued.
For any further information on the BoE or the activities of the BMP initiative – including its MEP Interest Group – please do not hesitate to contact EFNA at: advocacy@efna.net
For more contact:
Tadeusz Hawrot
EFNA Senior Advocacy Coordinator
advocacy@efna.eu
Elizabeth Cunningham
EFNA Communications Manager
communications@efna.eu
Apr 9, 2019
This year’s main theme for SAFE’s campaigning work is Life After Stroke, the issues around it and how the stroke survivors and their families are coping with it. The campaign will cover this year’s European Stroke Awareness Day in May and will culminate on October 29, for the World Stroke Day, when SAFE will present the Economic Impact of Stroke in Europe Report.
Stroke is responsible for 9% of all deaths each year in the EU and it is also the largest cause of adult disability. Total costs for stroke were estimated at €64 billion across Europe in 2010 and yet it is hugely under-funded in comparison to other chronic conditions. The most important risk factors for stroke are age, high blood pressure, obesity and diabetes, all of which are rising in a larger and increasingly elderly population living unhealthy lifestyles. Recent modest improvements in acute care mean that more people are surviving stroke, but with impairment, with the consequence that we have a major health economic and social burden catastrophe waiting to happen. This will severely impact all EU countries but especially those where inequalities in stroke healthcare are already known.
In 2017, SAFE has commissioned a research project on the economic impact of stroke in Europe. A health economics team from the University of Oxford is now finalising the report, which will be launched by SAFE in October 2019, for the World Stroke Day.
In anticipation of the final results, SAFE would like to remind the public that the absolute number of people living with disability from stroke has been increasing over the past three decades, and this is projected to increase. LMICs (low and middle income countries) have been disproportionately affected by stroke, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) from stroke have been generally increasing in LMICs.(1)
For this reason, SAFE is opening a conversation stream with leaders of our member organisations from 30 European countries. Each week, our readers will have an opportunity to read about one burning life after stroke issue in different countries. The series of interviews will shed light on specific country by country needs of stroke survivors and their families.
The slogan of this year’s campaign is: A life saved must also be lived, by Grethe Lunde from Norway, a Stroke Survivor and SAFE Board member.
(1) Feigin VL, Norrving B, Mensah GA. Global Burden of Stroke. Circ Res. (2017) 120:439–48. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308413
Apr 4, 2019
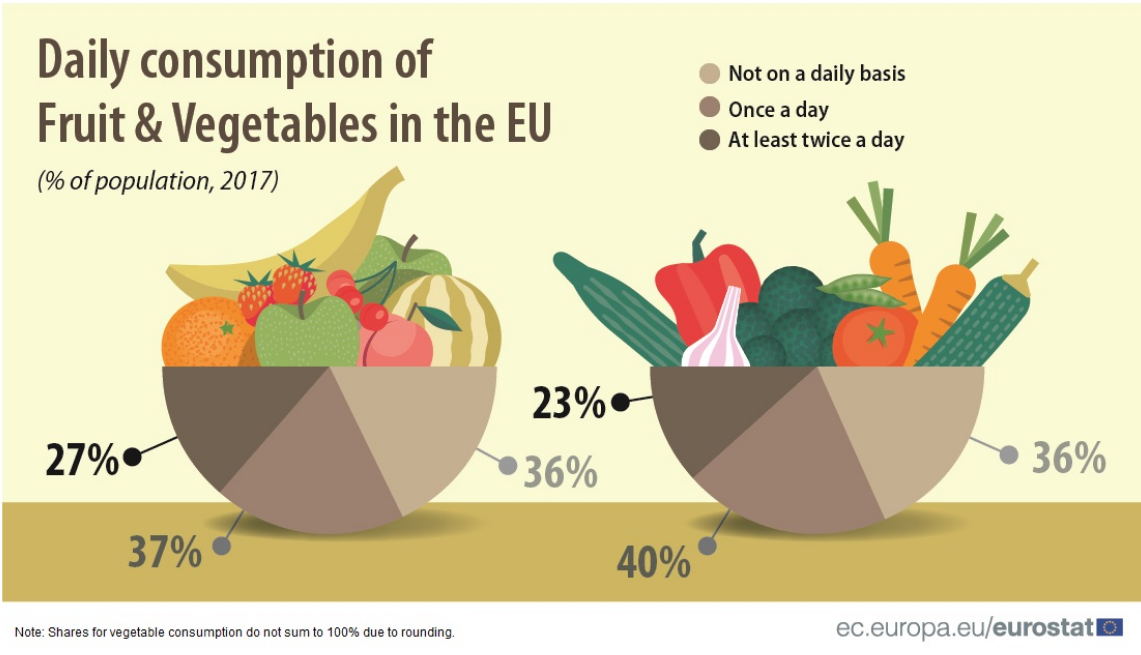
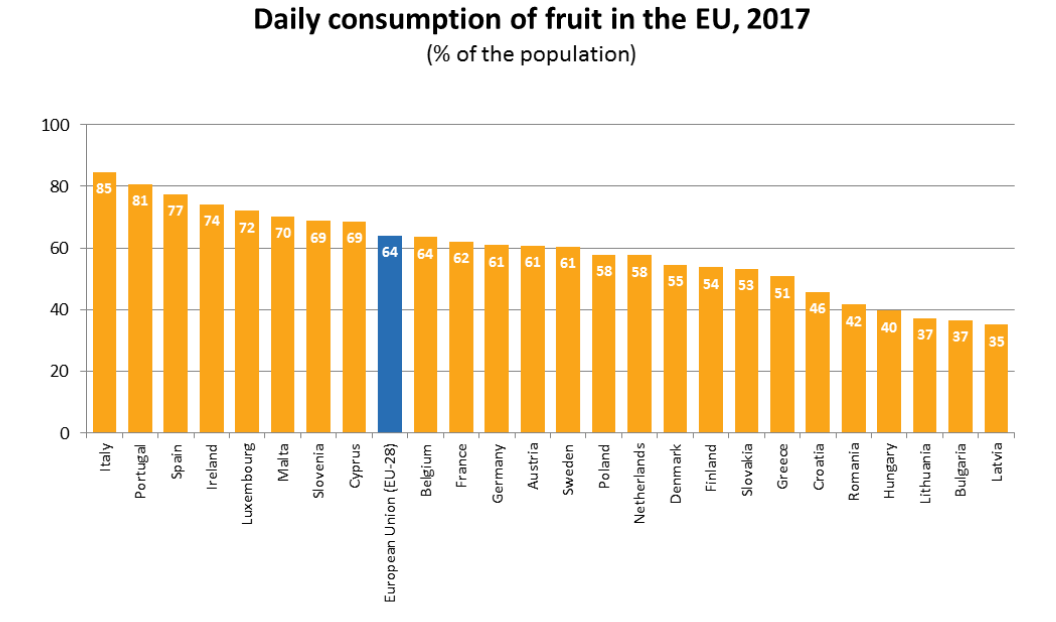
In 2017, around 1 in 4 people (27 %) ate fruit at least twice a day, according to a survey of the European Union (EU) population. A further 37 % of the EU population ate fruit once a day and the remaining 36 % ate fruit either less frequently or not at all during a typical week. Compared with fruit consumption, a slightly smaller proportion (23 %) of the EU population ate vegetables at least twice a day, and a slightly higher proportion (40 %) ate vegetables once a day. Among the EU Member States, daily intake of fruit was most prevalent in Italy (85 % of the population) and in Portugal (81 %).
The source data are here.
In contrast, in three Member States less than 40 % of the population ate fruit on a daily basis: Latvia (35 %), Bulgaria and Lithuania (both 37 %). When it comes to vegetable consumption in the Member States, Ireland and Belgium had the highest proportion of the population who ate vegetables at least once a day (both 84 %). While in most Member States between 50 % and 80 % of the population reported that they ate vegetables daily, there were five Member States where the proportion was below 50 %: Hungary (30 %), Romania (41 %), Latvia (44 %), Lithuania and Bulgaria (both 45 %).
For more information from this report, please click here.

Mar 28, 2019
Brussels, 28 March 2019- The Stroke Alliance for Europe (SAFE) organised today the event ‘Joining forces to prevent and control non-communicable diseases: The role of policy in tackling stroke’, under the patronage of the Romanian Presidency of the Council of the European Union, in Brussels, at the European Committee of the Regions. The event was organised by SAFE in collaboration with the European Stroke Organisation and the Romanian National Stroke Association.
The panel participants have put many proposals on the table. The most important request is for forming a stroke related sub-group for the purpose of facilitating the implementation of the Stroke Action Plan for Europe, the same as has been done for cancer and mental health.
As Jon Barrick, SAFE President stressed in his opening speech, the topic discussed today is of extreme importance: Stroke is the second most common cause of death in Europe, with nearly one hundred thousand (988,000) deaths each year[1]. In Europe, over 13% of women and 9% of men die from this disease (data from the MEP Hearth Group of the European Parliament).
 In 2018, SAFE and ESO released the “Stoke Action Plan for Europe 2018-2030”, which proposes a holistic approach to stroke management, from prevention to acute care, rehabilitation and life after stroke. The report sets out minimum targets to be reached by every European country, to equilibrate the quality of care across Europe.
In 2018, SAFE and ESO released the “Stoke Action Plan for Europe 2018-2030”, which proposes a holistic approach to stroke management, from prevention to acute care, rehabilitation and life after stroke. The report sets out minimum targets to be reached by every European country, to equilibrate the quality of care across Europe.
“Romania is definitely trying to put an end to inequalities in stroke care across the country, and we hope to see the same thing achieved at European level” said Tiberius-Marius Brădățan, Secretary of State, Ministry of Health of Romania. “We think that this is now possible thanks to the Stroke Action Plan for Europe that SAFE and ESO have released. If implemented, the Action Plan will underpin the step change in stroke care that is required to reduce the devastating impact that this condition has on individuals, their families and Member States’ economies.”
Effective healthcare planning and adequate resource allocation across Europe is needed to deal with this public health challenge, taking into account that the emotional and financial burden of stroke is largely borne by stroke survivors themselves and their families.
“Stroke remains a major cause of disability and death, but the opportunities to curb the effects of stroke have dramatically improved”- said Prof. Bo Norrving, who chaired the European Action Plan for Stroke 2018-30 steering committee, adding “While we are discussing the implementation of the European Stroke Action Plan, strokes continue to occur, and patients continue to get substandard care – becoming disabled or dying. Time to go from table to practice is now!”
Sorin Tuță, Vice-president of the Romanian National Stroke Association (ANRS), said that although Romania faces 61.500 new strokes each year, things have significantly improved in the past several years, especially in the domain of the acute stroke treatment, with 32 new stroke ready hospitals in 2019.

SAFE President and the representatives from the Romanian EU Presidency
“Romanian Registry for Interventional Treatment in Stroke was established in 2014 and stroke patients are treated almost exclusively by neurologists” stressed out Cristina Tiu, President Elect of the Romanian Neurology Society.
Prof. Tiina Laatikainen, from the Institute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, Finland, said that, even though the emergency care well organized and those hospitals not having neurologists 24/7 achieve consultancy by telestroke service, there are still challenges, such as endovascular treatments not available 24/7 in the whole country due to lack of angioradiologists, less than 15 % of patients achieve adequate rehabilitation and every fourth working aged stroke patient do not return to work (disability pension).
Thanking all discussion participants and the EU Romanian Presidency and the Committee of Regions for their support, Jon Barrick concluded the session by saying: “We have the scientific community and patients aligned. We have the will of European, national and regional decision-makers, and industry partners who are here today to give their support to future activities aimed at improving stroke prevention, treatment and research. I would therefore like to call upon the future European leaders, and upon the Member States, to work together to achieve the 2030 goals as set by the “2030 Stoke Action Plan for Europe.”

[1] Stroke is also the second most common cause of death in the EU, with over 425,000 deaths each year.

Mar 15, 2019
This text was was first published on www.svds-at-target.eu
In November 2018 the Zoom@SVDs study included the 60th participant, thereby reaching its milestone for midterm recruitment. The Zoom@SVDs study is an observational study that aims to advance our understanding of Small Vessel Disease, a condition in which the small blood vessels in the brain are damaged. We do this by zooming in on the small vessels with one of the strongest MRI scanners currently available for humans, located in the UMC Utrecht.
This study builds on a collaboration between the LMU in Munich (Germany) and the UMC Utrecht (Netherlands). In order to undergo a scan in the strong MRI in Utrecht, the 28 participants that were recruited so far in Munich travelled from all over Germany to Utrecht for an additional visit. Of course, the logistics of this study are very challenging, because flight tickets, train tickets and hotels have to be arranged as well. Also, all study information needed to be officially translated from Dutch to German and the researchers in Utrecht had to refresh their German language skills. However, these joined efforts have resulted in fast recruitment with happy participants and high-quality data.
Analyses of the first patient data have just started, of which we aim to publish the first results in the coming year. Of course, we will continue our recruitment and will continue to work in close collaboration. This study builds on our dedicated participants and good teamwork; thanks to all involved!

 Mark started the Stroke Stories podcast to seek out and hear from stroke survivors.
Mark started the Stroke Stories podcast to seek out and hear from stroke survivors.

 The BoE outlines clear focus areas and proposes recommendations for policy actions, which, if implemented, would significantly improve quality of life for people with neurological and chronic pain disorders, as well as their families and carers.
The BoE outlines clear focus areas and proposes recommendations for policy actions, which, if implemented, would significantly improve quality of life for people with neurological and chronic pain disorders, as well as their families and carers.



 In 2018, SAFE and ESO released the “Stoke Action Plan for Europe 2018-2030”, which proposes a holistic approach to stroke management, from prevention to acute care, rehabilitation and life after stroke. The report sets out minimum targets to be reached by every European country, to equilibrate the quality of care across Europe.
In 2018, SAFE and ESO released the “Stoke Action Plan for Europe 2018-2030”, which proposes a holistic approach to stroke management, from prevention to acute care, rehabilitation and life after stroke. The report sets out minimum targets to be reached by every European country, to equilibrate the quality of care across Europe.





