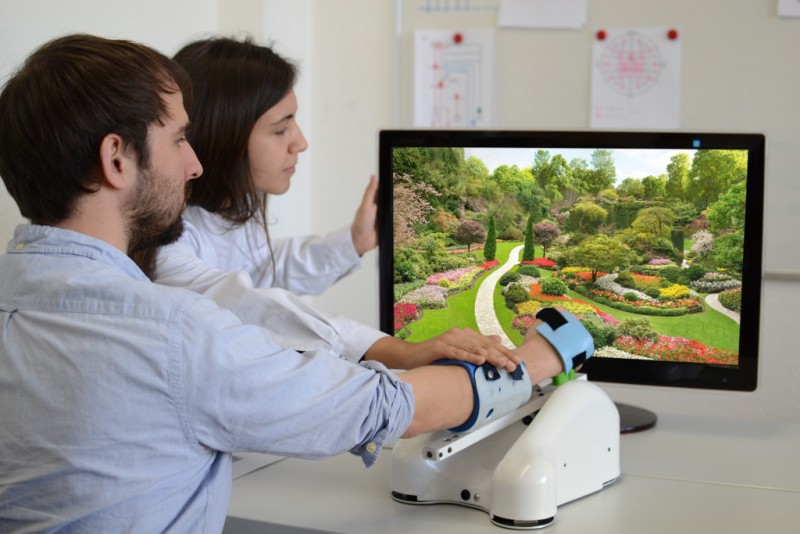

Aug 23, 2019
Project AMoRSA
AMoRSA stands for “Adaptive and highly motivating platform for the rehabilitation of patients with arm palsy following a stroke“. The project kicked off on March 1st, 2017 (ending February 29th, 2020).
MOTIVATION
In Europe, millions of people live with chronic paralysis after a stroke. An efficient strategy for systematic rehabilitation measures that is suitable for everyday use can help patients regain their mobility and carry out important everyday activities such as eating, drinking or dressing without outside help.
GOALS AND PROCEDURES
The aim of the project is to enable stroke patients with complete arm paralysis to rehabilitate their mobility providing them with complete arm paralysis with efficient, highly motivating and systematic neurorehabilitation suitable for everyday use. For this purpose, a training system will be created whose central element is a brain-muscle-machine-interface, which controls an exoskeleton attached to the paralyzed arm. The movement feedback generated by the actuators reactivates compromised connections between brain and muscles closing the brain-to-muscle loop and producing functional neuroplasticity. In addition, the rehabilitation system is embedded in a digital health game that intuitively communicates health information and training progress to patients and continuously motivates them.
INNOVATIONS AND PERSPECTIVES
By combining an orthotic robotic system with a direct feedback function, a novel training system for neurorehabilitation will be developed and the first clinical pilot will be performed during the project. This rehabilitation environment enables chronically paralyzed stroke patients to participate in life without restrictions again.
SURVEY
The burden of stroke is dramatic at many levels and there is a lack of controlled clinical trials and cost/efficacy analyses to incorporate new methods into everyday clinical practices. Furthermore, in many of the new developments and therapies, there is a clear lack of stakeholders involved during clinical research to clinical trials and practice transition. Current trends in stroke rehabilitation include the use of robotics (mainly to compensate therapists shortage and increase of demand), the use of serious games (computer gaming, virtual and augmented reality) to increase patients’ engagement and intensity of training, the telerehabilitation (home-use video games and training and movement assessment gadgets) and the use of neural interfaces to re-activate dormant or to generate via neuroplasticity mechanisms, connections between brain and muscles. All these components are present in AMORSA project.
With this survey, we want to investigate the demographics of the steadily changing stroke survivors community (including not only patients but their caregivers and therapists), their common limitations, interests and their opinion about these new rehabilitation trends. Furthermore, we want to quantify the potential adoption of new-coming treatments/therapies based on these trends. We have designed 3 different surveys, one for the patients, another for their caregivers (family and relatives) and the last one for therapists (neurologists, physiotherapists, etc).
Patients: we want to quantify the a) impairment level of the patients, especially the chronic ones; b) their current involvement in treatment, prevention or assistive measures; c) their use of technology (TV, smart-phone, video-games, etc) and their technology literacy; d) expectation regarding new therapies based on the mentioned trends; e) acceptable duration and intensity of rehabilitation therapies based on the trends and their acceptance rate; f) social aspects within the stroke community (e.g. interest in patients forums); g) the cost/benefit or compromise of rehabilitation measures based on the trends (e.g. acceptable specifications of an implanted solution for rehabilitation or assistive technology and the movement restoration achieved); h) interest in home-based rehabilitation gadgets based on the trends.
Care-givers: we want to quantify the almost the same as for the patients but from their perspective (normally we have observed a significant difference in perception in aspects of interest, motivation, impairment, etc);
Therapists: we want to quantify their a) demographics and skills; b) the clinical assessment scales (e.g. ARAT, MRC, NIHSS, Fugl-Meyer) and rehabilitation methods used (e.g. robots, mirror, group therapies); c) their service characteristics/limitations (e.g. number of patients per therapist, time per session etc); d) new therapies based on trends minimum requirement to be adopted (e.g. preparation time, easy to use etc); e) compensation limitation to accelerate the adoption of new therapies; f) relevance of predictor of recovery or biomarkers for patients stratification for rehabilitation therapies; g) their opinion on cost/benefit or compromise of rehabilitation measures based on the trends (e.g. acceptable specifications of an implanted solution for rehabilitation or assistive technology and the movement restoration achieved); h) interest in home-based rehabilitation gadgets based on the trends.
Please take part in this survey by clicking on these links below:
Patients: https://www.soscisurvey.de/amorsa_reha1/
Relatives / caregivers: https://www.soscisurvey.de/amorsa_reha3/
Therapists: https://www.soscisurvey.de/amorsa_reha2/

Aug 23, 2019
This week, Inese Maurina from Latvian organisation Parsirdi.lv, offered SAFE team an insight into the needs of the Stroke Survivors and #LifeAfterStroke issues in her country.
SAFE: What is one issue related to the life after stroke in your country that you think needs special attention?
IM: I would like to stress two things:
1) Rehabilitation – there are long waiting lists to get the rehabilitation services after stroke. Patients and their relatives are also confused because of lack of sufficient information on where to go, what to do next, where to look for help, where to get rehabilitation services, etc.
Due to these reasons lot of patients receive rehabilitation too late or not as much as needed.
2) Availability of medicines and patient adherence
Increasingly effective medications are available for the prevention and treatment of stroke risk factors, but often patients cannot afford to pay for them, so they stop taking them or even do not start to use medicines. This leads to very serious consequences – illness, disability or death. Similarly, many patients do not qualify for medication reimbursement due to very strict requirements.
According to data of Stroke Units, there are many patients who return to the hospital and one of the reasons is discontinuation of medication. This is due to both – the financial capacity of the patients and also the lack of understanding of the need for medication and poor cooperation with their physicians and specialists.
SAFE: What would be the solution, i.e. what is your organisation’s position regarding this issue?
IM: Not only stroke has serious health consequences, but it also has a very heavy social and financial burden on patients, their families and society as a whole. According to estimates of the Latvian Health Economics Association, patients and their relatives bear almost one third of the total cost of stroke treatment in Latvia, which is over 70 million euros per year. According to health economists, such a “co-payment” for stroke patients is too high given the high rates of disease mortality and disability. The burden of the disease on the social security budget could be substantially reduced by ensuring timely stroke prevention, treatment and quality rehabilitation.
It would be important to increase the healthcare budget spent on the post-stroke rehabilitation services in order to make this service available to all patients and without long waiting lists. There is also a need for specialists and innovative technologies to improve the rehabilitation services in Latvia. It would be also important to develop clear patient pathways information materials to be disseminated to both stroke units and GPs.
The health budget for stroke prevention needs to be increased, as it will reduce the number of sudden strokes and thus require lower treatment, rehabilitation and disability costs. There is a need to increase also budget for innovative and effective medical medicines and to improve the collaboration of patients and doctors in order to increase the patient adherence.
SAFE: Please tell us more about your organisation.
IM: ParSirdi.lv is non-governmental organization founded in 2011, bringing together various heart and cardiovascular disease patients and their relatives. Our mission: to reduce the impact of heart and cardiovascular diseases by promotion of healthy living, educating society regarding the risks of diseases, ensuring the access to health care information and advocacy of patients.
Our aims are:
Protecting the rights of cardiovascular patients to access quality medical care (medicines, devices and services);
Identify and reduce factors that prevent patients with cardiovascular disease from receiving quality healthcare;
Improve the quality of life of people with cardiovascular diseases through active involvement in the development of national cardiovascular policy, in cooperation with state and municipal institutions;
Facilitate the exchange of information between patients, medical professionals and the public with the aim of helping patients with cardiovascular disease to successfully organize their daily lives, integrate into public life, and achieve professional success;
Carry out educational work to raise awareness among cardiovascular patients and the general public about cardiovascular disease, its prevalence, risk factors and treatment;
Promote a healthy lifestyle;
Develop projects to improve the quality of life of patients with cardiovascular disease.
Since 2013 patient organization ParSirdi.lv is an associated member of the international organization SAFE (Stroke Alliance for Europe).

Aug 23, 2019
Do you or someone you know have experience with spasticity and Botulinum Toxin Type A injections?
SAFE invites you to participate in an international survey, conducted by Carenity, an online patient community, and biopharma Ipsen to help advance medical research and improve the lives of other patients.
Both patients and caregivers of patients with spasticity due to stroke (as well as traumatic brain injury or spinal cord injury) who are currently receiving Botulinum Toxin Type A injections or who have stopped receiving these injections less than a year ago can participate.
Botulinum toxin effect usually peaks around 4 to 6 weeks after injection, then it slowly decreases. This decrease is called the waning of botulinum toxin effect. The aim of this survey is to better understand patients’ experience with botulinum toxin type A injections, in particular:
– to better understand how patients experience the waning of botulinum toxin type A effects
– to identify the impact of the waning of botulinum toxin type A effects on the patient’s quality of life
– to describe patient populations profile
– to assess the reasons for stopping botulinum toxin type A injections
This survey will be the subject of communications during scientific congresses or scientific publications that will be redacted in collaboration with an international team of medical experts.
A synthesis of the results will be made available after the publications.
This international survey is conducted in Europe (France, Germany, Italy and the UK) and in the US until September 13th.
It is available in 4 languages:
English: https://member.carenity.co.uk/newSurveyBymail/0/38/0/0
French: https://membre.carenity.com/newSurveyBymail/0/107/0/0
German: https://member.carenity.de/newSurveyBymail/0/26/0/0
Italian: https://member.carenity.it/newSurveyBymail/0/25/0/0
Thank you very much for your participation!
Participation in this survey is unpaid.
To find out more about how your data will be processed and how to exercise your rights, read the survey information page, accessible when you click on the link provided above in this text.

Aug 21, 2019
First published on ARNI Institute for Stroke Rehabilitation website
A change in cognitive ability is common after a stroke. Did you know that as many as two-thirds of stroke survivors may experience cognitive impairment as a result of their stroke.? If this is you, or you know someone who seems possibly to be going through such difficulties, here’s 18 steps you can take to try and improve cognition difficulties after stroke:
First, what is cognition?
Put simply, cognition is thinking; it is the processing, organising and storing of information – an umbrella term for all of the mental processes used by your brain to carry you through the day, including perception, knowledge, problem-solving, judgement, language, and memory. The brain’s fantastic complexity means that it can collect vast amounts of information from your senses (sights, sounds, touch, etc) and combine it with stored information from your memory to create thoughts, guide physical actions, complete tasks and understand the world around you.
A stroke can affect the way your brain understands, organises and stores information. This brain injury can result in damage to the areas of the brain that are responsible for perception, memory, association, planning, concentration, etc. The severity and localisation of the stroke will effect the type and level of difficulties experienced by an individual, and will vary from person to person.
It can be difficult to plan and organise daily tasks. The brain is constantly working in the background, allowing us to complete a task based on prior knowledge, experience, and learned behaviour.
You don’t have to consciously think how to boil the kettle, change TV channels or put on your socks before your shoes: you just do it. But damage to the brain can result in problems with these planning and execution mechanisms.
You might not be able to think how to do a simple task, or you may get the sequence wrong (for example, shoes before socks). You might have trouble with orientation, which could include not knowing the date, day of the week, or even who you are with. Problem-solving too can become difficult. Making decisions, solving problems, understanding numbers and managing money can be a challenge.
Good cognitive function also relies on memory. The brain uses 2 types of memory to hold information, the long and short term memory. Short-term memory is the temporary store for small amounts of information. This information is kept readily available and can be recalled quickly. For example, a phone number can be remembered long enough for you to dial it. Long-term memory is where you keep your experiences, thoughts and feelings from the past and things stored here can be stored indefinitely. Memory problems could result in difficulty storing or recalling information. This could include problems remembering appointments, important dates or in the case of short term memory, what you were about to do, or what somebody just said to you.
Problems with concentration are common. Concentration is required for effective cognitive function, as many of your thinking process require concentration. Concentration requires our brain to filter out much of the information coming in from your conscious thinking, so you are not distracted by it.
Stroke can impact on this ability because of damage to the areas of the brain responsible for this, and also because tiredness, pain and emotional problems have an effect of the ability to stay focused and concentrate. This could result in difficulties when trying to follow a television programme, or conduct a conversation with a friend. Multi-tasking too is difficult.
18 Things to try
- Cognitive problems are confusing and frustrating. But, there are some things you can to do help. Most improvements occur in the first 3 months after a stroke, after which they slow down, but the brain will keep creating new neural pathways after this time.
- To help with memory and perception problems, try using a diary, day planner, calendar or notepad. Writing down appointments and creating to-do-lists can help you to remember them.
- Photos and pictures can help to ‘trigger’ your memory.
- Check your calendar, newspaper or diary to help you remember the day and date.
- Make notes of important conversations.
- Use notes, lists and labels around the house and help prompt you to remember. Mobile phones are a great resource. Set alarms, reminders and memos to remind you throughout the day.
- It is important not to overload yourself, finish one task before you start another. Plan your day and prioritise tasks.
- Try slowing the activity down, working through a step at a time.
- Keep instructions clear and short, no more than 5 or 6 words to a sentence, and only 1 or 2 instructions at a time.
- …
Please read the full list here.

Aug 16, 2019

Eva Pettemeridou, PhD, Clinical Psychology
Eva Pettemeridou from the Cyprus Stroke Association spoke this week with SAFE team about Stroke Survivors’ needs and #LifeAfterStroke in her country. She pointed out the lack of information and services after stroke as one of the most important issues.
SAFE: What is one issue related to the life after stroke in your country that you think needs special attention?
EP: One of the issues pertaining to life after stroke in our country is the lack of information and services following the initial stroke treatment and prognosis. Initially, patients and their families seem to be underinformed, if at all, on the effects of stroke for each individual case, and as an effect the importance of receiving in or out –patient rehabilitation. As a result, the individual returns home without receiving individually tailored treatment that will help in improving post-stroke deficits. Therefore, these individuals and their families return home with little awareness of what is to be expected from the patient cognitively, physically, and psycho-socially, and potential changes necessary for the individual to function independently.
SAFE: What would be the solution, i.e. what is your organisation’s position regarding this issue?
EP: The Ministry of Health can hire staff that can provide information on the importance of receiving rehabilitation based on the needs of each individual, and potential services provided in Cyprus. However, for this to be feasible the Cyprus Stroke Association (CSA) should focus its efforts in influencing all relevant authorities and stakeholders. This may be addressed via directly contacting politicians, writing newspaper articles, and using of social media to bring greater awareness. In addition, by establishing collaborations with different national and international organizations (incl. universities) and companies (e.g. rehabilitation centers, pharmaceutical companies), CSA may be able to further influence relevant authorities in providing maximum support to stroke survivors.
SAFE: Please tell us more about your organisation.
EP: The Cyprus Stroke Association (CSA) was founded on February 10, 2009 (Registration number 3419) and is a Non-Governmental Organisation acting within the Cypriot and European legislation. The vision of the CSA is to work towards the prevention of cardiovascular incidents in Cyprus and to offer maximum help and support to individuals who have suffered a stroke, their families and kin environment. The mission of the CSA is to prevent strokes, and reduce symptoms through information and education. The aim of the CSA is to identify high-risk individuals and inform them appropriately, access people with stroke and help them receive appropriate treatment and care and improve the quality of life of people with stroke and their families. We also aim to formulate existing legislations for people with stroke, provide information about their rights and the sponsorship offered by the state apparatus.
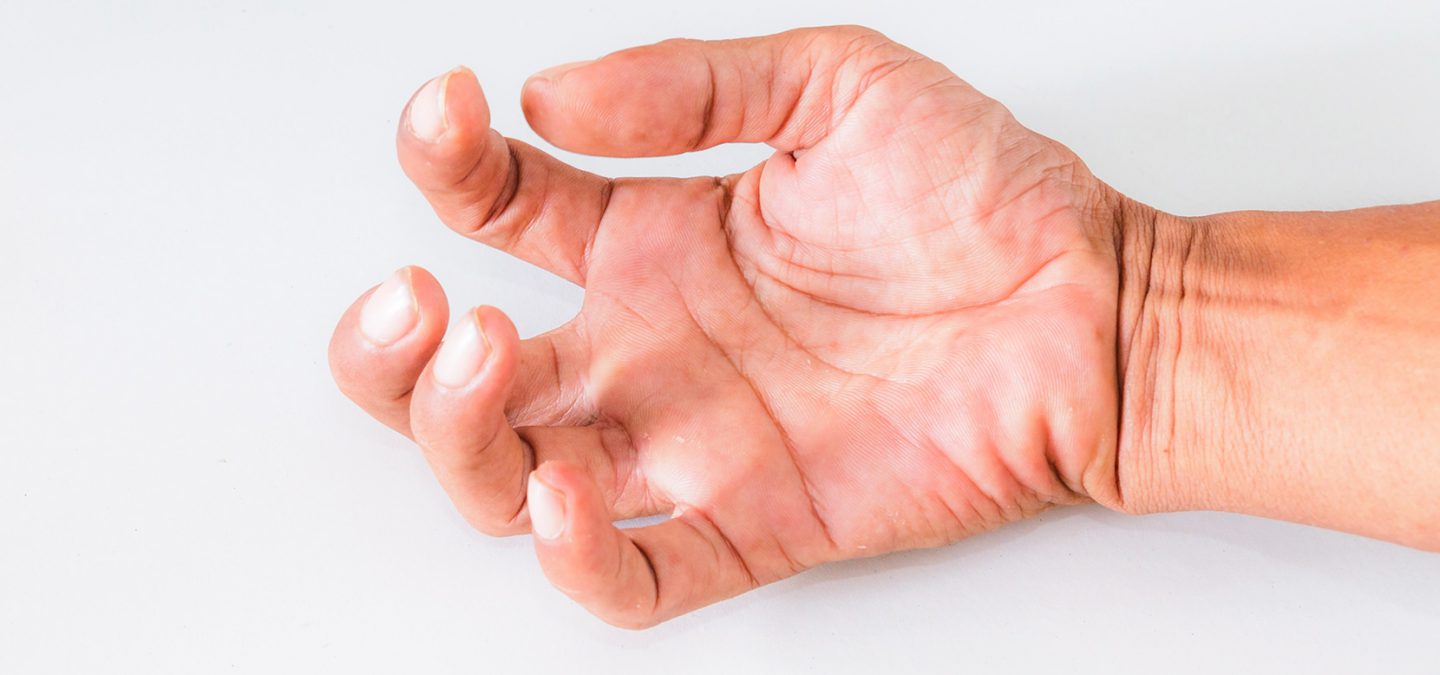
Aug 12, 2019
This article first appeared on arni.uk.com
Written by Tom Balchin
Upper limb spasticity is suffered by a full 70% of the stroke population, By three months post stroke 19% of people will experience spasticity and this figure increases to 38% of people after 12 months.
Did you know that it’s one of the biggest things that survivors tell consultants, GPs, family, carers and friends that they wish they could positively alter?
Spasticity can develops months or even a year after stroke — and often may become more noticeable as recovery moves on and can have a very significant bearing on your quality of life. Let’s look at what spasticity is:
Muscle stiffness;
Upper extremity hypertonia (excessive muscle activity);
Loss of fine motor control (for example small hand movements);
Paresis;
Soft tissue contracture;
Muscle overactivity leading to the reduced ability to relax;
Muscle spasms;
Changes in limb posture; and
Muscle fatigue.
Let’s see if you can grab some tips here to help you beat its limitations.
Spasticity is caused by miscommunication between your brain and your muscles. It has neural and non-neural components to it. Let’s delve deeper: knowledge is power,
Normally your muscles are in constant communication with your brain about how much tension they’re feeling, and the brain has to constantly monitor this tension to prevent tearing. Your brain continuously sends out messages telling your muscles when to contract and relax.
You can read the full article here.
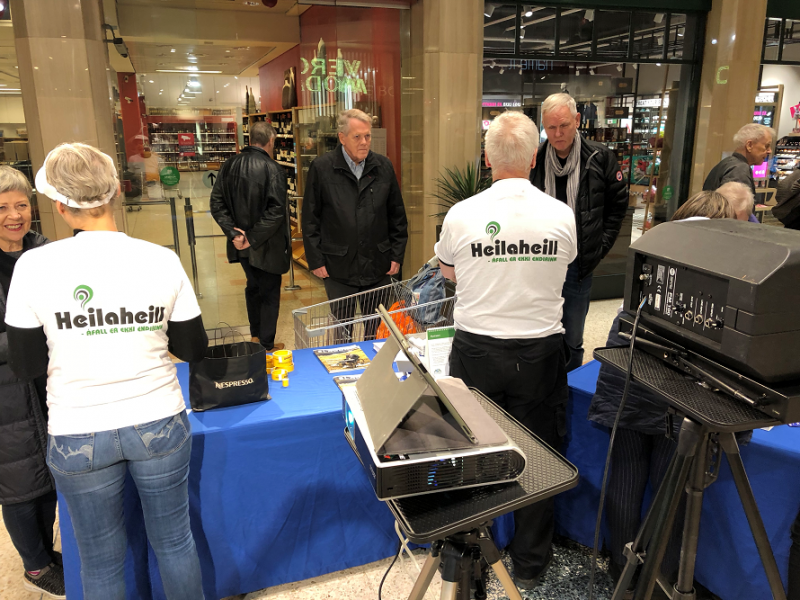

Aug 2, 2019
Caption: On the International Stroke Day 2018 our members HEILAHEILL, patients, neurologists, etc. to promote the disease and disseminate information to the public in KRINGLUNNI, Reykjavik’s largest shopping center, which attracted much attention. Chairman of HEILAHEILL Thorir Steingrimsson and the specialist in neurology (thrombectomy) Bjorn Logi Thorarinsson in National University Hospital of Iceland | LSH · Department of Neurology.
“According to circumstances in ICELAND we are unable to make significant survey on prevention, treatment and rehabilitation of the stroke or exploring the burden of the stroke because we have only 360.000 citizens. Therefor it is difficult for the authorities to answer our queries about the incidence of stroke across the country. But however we are trying to follow Stroke Action Plan for Europe 2018-2030 by taking the guidance of professionals and health authorities” says the Chairman of HEILAHEILL, Icelandic stroke support organisation, Thorir Steingrimsson.
SAFE: What is one issue related to the life after stroke in your country that you think needs special attention?
TS: Being in SAFE gives us the opportunity to compare ourselves with other health systems in other European countries regarding the stroke. Many things are similar to us and the other Nordic countries, but there are a number of factors that are similar to the burden of the stroke with other nations, for example there is a lack of follow-up from the healthcare system, when individuals are enrolled in the community. The main problem in our country is that the health authorities and ÖBÍ (The Organisation of Disabled in Iceland) which we accept money from, do not recognize aphasia after stroke as a special disability category in the healthcare system, but it is mixed with aphasia due to age or other trauma. The majority of those who have aphasia after stroke in our country do not experience themselves as ratifying the citizens of society. It is a great shame. Therefore, HEILAHEILL has worked with professional, speech therapists and other patient associations to raise the awareness of the health authorities and the public of this disability. We realize that this is starting to work, as the current government is beginning to recognize the problem i.a. support us financially specifically in equating education with this disability category
SAFE: What would be the solution, i.e. what is your organisation’s position regarding this issue?
TS: We still have opportunity to do many things, which larger nations find difficult to do, for example make a plan for decision party about stroke treatments over the hole country. In comparison, we can be likened to a little drill next to a big oil ship.
Healthcare professionals have done tremendous progress in thrombectomy, over the past two years in Landspítali in Reykjavík, which is the largest and leading factor in healthcare in the country and estimate it to be national 2020! HEILAHEILL has decided to introduce this improvement among the public and in the country and use this opportunity to raise public awareness of the first signs of stroke and and urges the public to push the government to put more money into reducing the burden of a stroke!
SAFE: Please tell us more about your organisation.
TS: HEILAHEILL is a independent companionship for stroke survivors with individual membership for the whole country. The company have opportunity to meet the decision-makers by the authorities face-to-face, and they have supported us in our policy and it is also close relationship between people In HEILAHEILL and professionals over the country.
Therefore there is compelling evidence in ICELAND that stroke is highly preventable, treatable and manageable, and there is a potential to drastically decrease the burden of stroke, including substantially reducing its long-term consequences. This requires the joint actions of Ministries of Health and Social Care, other governmental bodies, scientific and stroke support organisations, healthcare professionals, clinical and preclinical researchers and industry and most of all, a good and powerful communication with patient organizations.
The benefits of tPA in patients with acute ischemic stroke are time-dependent, and guidelines recommend a door-to-needle time of 60 minutes or less. Professionals in Iceland say the average has dropped from 80 minutes to 25 minutes in the last three years!
HEILAHEILL has released an app in smartphones with information on the first signs of stroke. And when it is inserted in the beginning you place your social security number, it makes it your personal safety button to the emergency line and they positioning the device with precision. The smartphone tells who is calling for help, age, gender, wherever you are in the country!

Jul 30, 2019
The celebrations of the 25th anniversary of the German Stroke Foundation officially ended on its birthday on January 29th 2019. Of course the work on many projects and events continues. Here are some examples.
New Case Manager for children with stroke
 The second “Case manager for children with stroke” (Schlaganfall-Kinderlotsin) was installed at the beginning of the year. Franziska Schroll works at the Schön Clinic in Vogtareuth (Bavaria) and will support families with stroke-affected children in southern Germany. The foundation “RTL – We help children” finances the project for two years.
The second “Case manager for children with stroke” (Schlaganfall-Kinderlotsin) was installed at the beginning of the year. Franziska Schroll works at the Schön Clinic in Vogtareuth (Bavaria) and will support families with stroke-affected children in southern Germany. The foundation “RTL – We help children” finances the project for two years.
The case manager provides information about stroke and helps families to get all the treatments, therapies and social support they need. The other case manager, Marco Vollers, continues his work in Bremen and is responsible for the northern part of Germany.
Seminar for parents
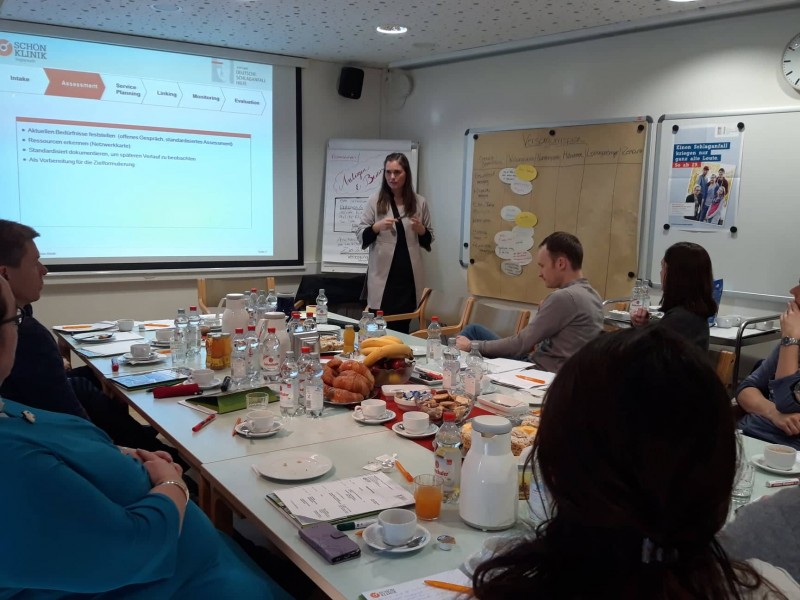

When a child has a stroke, the parents have many questions. Which therapy is best? Which lasting consequences will the stroke have? Will my child need special support at kindergarden or at school? How will the family cope with the difficult situation? Experts answered these questions at a seminar for parents. Parents had the chance to get general information about stroke and discuss their individual situation with doctors and therapists.
Stroke-scan “in jail”

Many people have high blood pressure or diabetes and don’t know about it. This is why the German Stroke Foundation offers to scan the risk of stroke at work. At the beginning of the year the testing took place in a very special location: in jail.
Jail-employees had the chance to test their risk of stroke and discuss stroke prevention. Alexander Leipold, former professional wrestler and ambassador of the foundation, talked about his rehabilitation and motivation after the strokes.
Workshop for leaders of self support groups
The foundation offers workshops for leaders and spokespersons of self support groups. In 2019 they took place in Hamburg, Halle and Zwickau. The participants learn for example about new laws, how to finance their group, how to use social media and discuss many questions. The workshops help them to be up to date and pass important information on to the other group members.

Case Management Symposium
The project “STROKE OWL” is continuing successfully. Professional case managers support stroke survivors in the region Ostwestfalen-Lippe (OWL = East part of Westphalia covering 2 million inhabitants) for one year.
With this project the foundation wants to proof that a close support after the stroke can improve the quality of life of stroke patients and reduce the risk of further strokes. 1,5 years into the project the foundation organised a symposium for case management experts to discuss the outcomes and challenges to date.

Stroke in daily soap
“Unter uns”, a popular German daily soap on RTL-television, picked up stroke as a topic in the storyline. One of the main characters gets a stroke and suffers from paralysation and aphasia afterwards. The foundation supported and advised the crew. Actors visited the foundation and spoke to stroke patients to prepare for their roles and employees of the foundation gave advice on the script.
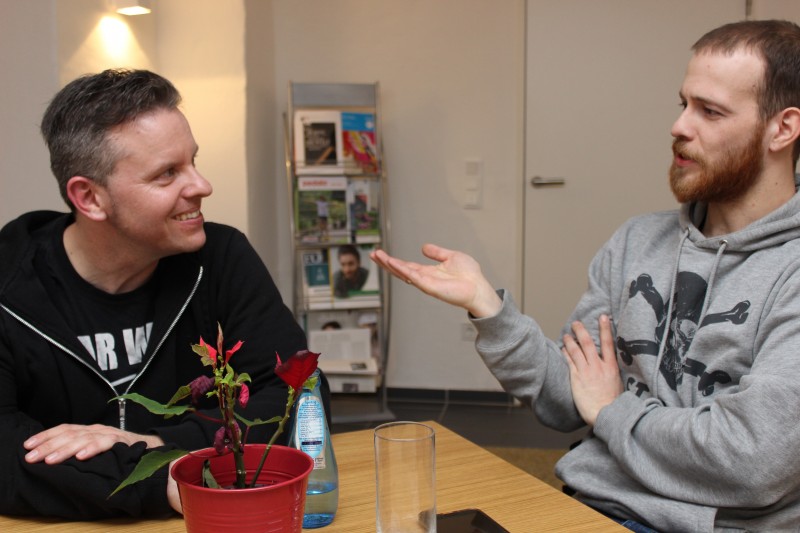

Photo: Stroke survivor Sascha Stachorra (left) helps actor Patrick Müller to prepare for his role.
Volunteer stroke-helpers
Volunteer stroke helpers support stroke survivors in their every day life. For example they get groceries together, accompany them for a walk or play board games. More and more people are interested in working as a volunteer in this field. This is why the foundation supports courses of instructions all over Germany. Local partners help organising the project, which is now offered in twelve regions.

Day against stroke
 The national “Day against stroke” on May 10th is one of the most important days for communication about stroke related topics. The motto in 2019 “I feel something you can’t see…” is based on the German name of the child’s game “I spy with my little eye.”
The national “Day against stroke” on May 10th is one of the most important days for communication about stroke related topics. The motto in 2019 “I feel something you can’t see…” is based on the German name of the child’s game “I spy with my little eye.”
Main goal was to focus on the unseen consequences of stroke like difficulties to recall information or to concentrate, neglect, visual field fail and emotional changes. Many newspapers, TV- and radio stations reported about the topic and it was successfully spread across social media. #Taggegendenschlaganfall (#dayagainststroke) made it into the top 10 hashtags on twitter in Germany for the first time.

Jul 30, 2019
First published on ScienceDaily.com
Aging men with low testosterone levels who take testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) are at a slightly greater risk of experiencing an ischemic stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), or myocardial infarction, especially during the first two years of use, reports a study appearing in The American Journal of Medicine, published by Elsevier. The findings confirm concerns voiced by many health agencies about the potential risks associated with the treatment.
The study analyzed a large database of electronic medical records of patients enrolled in primary care practices in the United Kingdom and formed a cohort of 15,401 men, aged 45 years or older, with low testosterone levels (hypogonadism). Users of TRT had a 21 percent greater risk of cardiovascular events compared with nonusers, corresponding to an additional 128 events. The increased risk appears to be transient, declining after two years of TRT use, which the investigators attribute to a phenomenon called “depletion of susceptibles.”
“Our findings show that the use of TRT was associated with an increased risk of stroke, TIAs, or cardiac arrest during the first two years of use,” noted Christel Renoux, MD, PhD, Centre for Clinical Epidemiology, Lady Davis Institute for Medical Research, Jewish General Hospital; and Departments of Epidemiology, Biostatistics, and Occupational Health, and Department of Neurology and Neurosurgery, McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada. “There is limited evidence on the long-term clinical benefits of TRT to effectively treat the modestly declining levels of endogenous testosterone levels of aging but healthy men. We strongly recommend that clinicians proceed with caution when considering prescribing TRT and first discuss both the potential benefits and risks with patients.”
Please read the full article here.

Jul 26, 2019
“The life of stroke victims is made difficult in several aspects. It is not only the physical handicap, but also a state of desolation. Family members can act against these troubles with good vigor and vitality, nevertheless a support of the surrounding society would be much helpful.” says Prof. Pavel Kalvach from Czech stroke support organisation Sdružení pro rehabilitaci osob po CMP (Czech Association for stroke victims).
SAFE: What is one issue related to the life after stroke in your country that you think needs special attention?
PK: This is a point, which we should stress in our Czech community: more clubs for stroke victims, for stroke carers, more encouragement in terms of mutual communications, music, creative activities. The people affected by stroke can produce these activities partly on their own, but they need necessarily organizational as well as logistic support. Given such meetings would be established, we could believe, that they could then run already spontaneously. Certainly much enthusiasm is needed to put these intentions into reality.
SAFE: What would be the solution, i.e. what is your organisation’s position regarding this issue?
PK: The Czech Association for rehabilitation of stroke victims provides counselling, provides courses, activates clubs throughout the country, but its reach is by far insufficient. Many healthy, retired people, who could actively contribute to the care of those less happy in their physical health state, ignore the needs of stroke individuals and thereby also their eventual personal pleasure of making good deeds. Our organization should be more proactive in sharing knowledge and encouraging people in those activities. Self-supporting groups could be conceived and we should reach out to put them in life.
SAFE: Please tell us more about your organisation.
PK: The activity that the Czech Association for stroke victims takes the most merit for is the arrangement of summer camps, aiming at rehabilitation. These courses occur in recreational regions of Czech republic. Care of physiotherapists, of medical doctors, psychologists and logotherapists is provided for groups of approximately 40 persons. These courses are financially supported by our Ministry of health, who would cover ½ of the expenses. The other ½ is covered by each person himself. Besides of the medical and psychological individual and group training also cultural activities are organized, like visits to the sightseeing around, or collective singing, or even dancing. People take great pleasure in such course, but the number of those, who achieve to participate is still too low: About 200 per year. If we compare this with the prevalence of stroke victims in Czech Republic, this number make less then 5% of people, who could profit.










 The second “Case manager for children with stroke” (Schlaganfall-Kinderlotsin) was installed at the beginning of the year. Franziska Schroll works at the Schön Clinic in Vogtareuth (Bavaria) and will support families with stroke-affected children in southern Germany. The foundation “RTL – We help children” finances the project for two years.
The second “Case manager for children with stroke” (Schlaganfall-Kinderlotsin) was installed at the beginning of the year. Franziska Schroll works at the Schön Clinic in Vogtareuth (Bavaria) and will support families with stroke-affected children in southern Germany. The foundation “RTL – We help children” finances the project for two years.





 The national “Day against stroke” on May 10th is one of the most important days for communication about stroke related topics. The motto in 2019 “I feel something you can’t see…” is based on the German name of the child’s game “I spy with my little eye.”
The national “Day against stroke” on May 10th is one of the most important days for communication about stroke related topics. The motto in 2019 “I feel something you can’t see…” is based on the German name of the child’s game “I spy with my little eye.”




