
Jun 27, 2019
FAST HEROES 112 is a stroke intervention that does not only educate children and their extended families to recognize stroke symptoms but also aims to enhance the relationship between children and their grandparents (or Grandheroes as we call them). To date, three schools have taken part in the program in Thessaloniki, Greece with encouraging results. During the first stage of the piloting phase, kindergarteners participated in a wide range of activities over a period of 5 weeks revolving around four superheroes. These activities taught them to recognize some of the main stroke symptoms and appreciate the importance of calling an ambulance on 112 if stroke is suspected. Results from our first systematic study revealed successful outcomes and gave rise to additional interventions in two more schools.
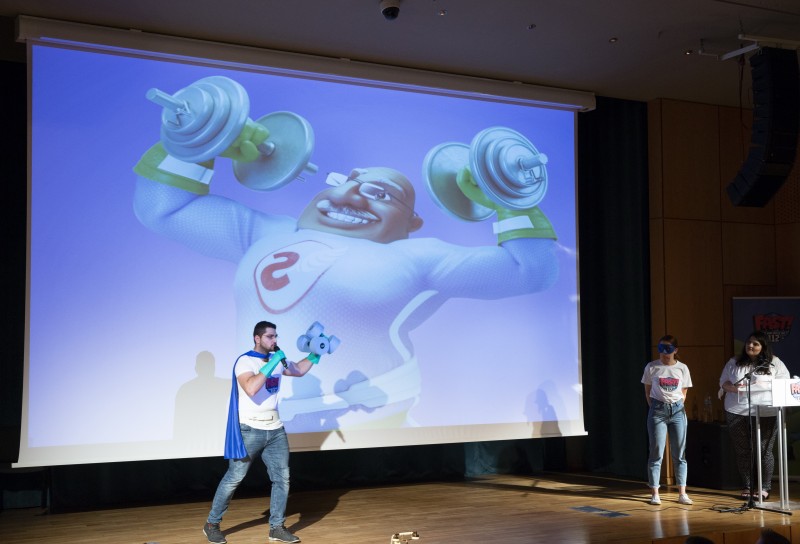

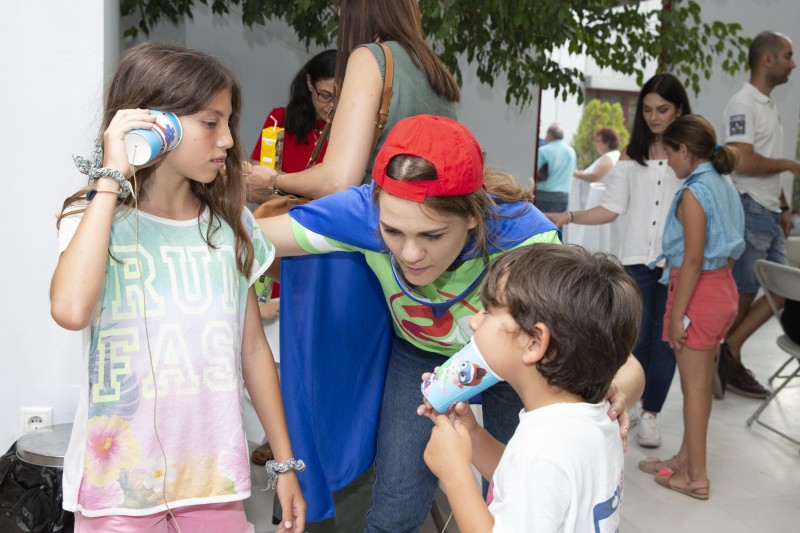
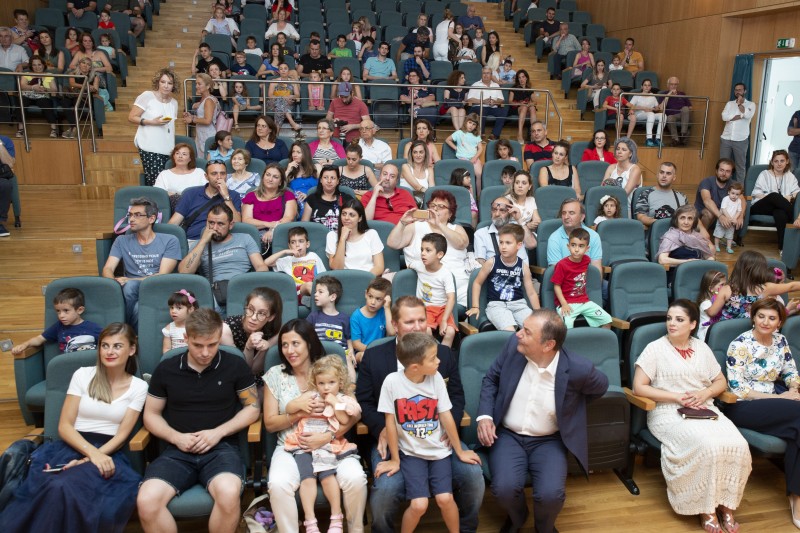
Around 200 people; all children and family members from the 3 participating schools, met on Thursday 20 June for Grand Hero Day celebration. The event, organized by Panorama Town Hall in Thessaloniki, Greece hosted a series of activities, continuing to educate children and families but also disseminating the aims and outputs of the program to the public. Parents from the three schools gave a very enthusiastic response to Grand Hero Day and additional interest was expressed by other schools in Greece for participating in the program in the next academic year.

FAST HEROES 112 is next travelling to Bulgaria! On Friday 21 June, FAST HEROES 112 team members and two participants from Bulgaria had the opportunity to discuss the content and structure of the existing program, its aims and objectives, as well as its current and future feasibility. Our team drew our new collaborators’ attention to effective strategies to be adopted and pitfalls to be avoided.
As public involvement is growing and more active international collaboration is being fostered, FAST Heroes 112 under the guidance of the University of Macedonia and with support from the Angels Initiative is hoping to inspire others to empower young heroes and unleash their potential to save their own heroes.
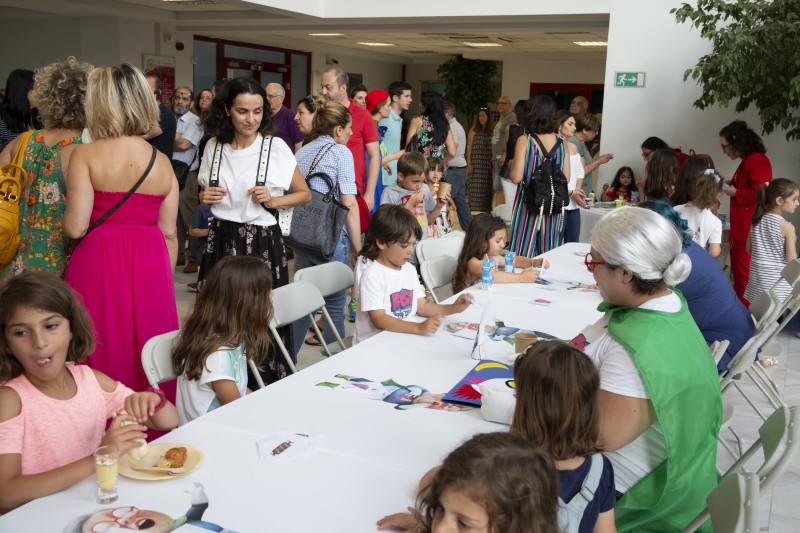

Photo credits: Angels Initiative

Jun 25, 2019
PRESTIGE AF is a €6.9m project, aimed at patients with atrial fibrillation (AF), a common heart condition which causes irregular and abnormally fast heartbeat, who have previously had a stroke caused by bleeding in the brain (termed intracerebral haemorrhage or ICH). The Prevention of Stroke in intracerebral hemorrhage survivor with Atrial Fibrillation (PRESTIGE-AF) brings together scientists and clinicians across Europe with the goal of reducing the risk of further stroke in this group of patients.
At the core of the PRESTIGE-AF project is a clinical trial to gather evidence around recommended medication for stroke prevention in patients with AF. Several sub-studies will explore individual predictive risk modelling using brain imaging, genetic testing and other biological markers. Other aspects of the project include exploring cognitive and psychological factors and drug adherence by patients.
Congratulations to the team at Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust (UK) who randomised the first participant into the PRESTIGE-AF Study, while other sites across Europe are underway to do the same.

The team at Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust who randomised the first participant. From left: Vaishali Dave, Peter Wilding, Ana Gil, Sheila Mashate (front-right). Congratulations to the team!
The Stroke Alliance for Europe (SAFE) has responsibility in the project for disseminating information about TENSION to the stroke community. For more information, please contact research@safestroke.eu.
PRESTIGE-AF has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 754517.

Jun 21, 2019
“The municipalities (in Norway) govern themselves regarding the economy and the government can’t earmark money to be used in the municipalities for each purpose. The municipal decides what they want to use the money for. And too often we see that there are no more money left when it comes to give patients the treatment they need, and which Norwegian law grants them” says Bjørn Bakke, leader of the Norwegian Stroke Support Organisation, Norsk forening for slagrammede, which is a member of SAFE.
SAFE: What is one issue related to the life after stroke in your country that you think needs special attention?

Photo: Bjørn Bakke, private archive
BB: In Norway we see that the situation for stroke survivors gets worse after the initial treatment in the stroke unit in hospitals and the first rehabilitation in the hospitals. These treatments (medical, surgery, rehabilitation) are financed by the government and follows in most cases national guidelines which are developed and refined during the (last) years. These treatments are usually of a very high quality.
The problem arises when the patient leaves the governmental treatment and the local municipal takes over the rehabilitation. There are of course laws regulating that a patient is granted the same treatment. But unfortunately, this is not necessarily so – in most cases. Norway has approx. 400 municipalities and every single one has a different approach to this issue. To be short, it comes down to economy.
SAFE: What would be the solution, i.e. what is your organisation’s position regarding this issue?
BB: There are 4 stroke organizations in Norway, and we have all concluded that we must engage politicians so that the parliament can pass new laws to strengthen the rights for the patients. This year we have local elections, and this gives us all a great opportunity to address municipal politicians all over Norway. We have a lot of work to do to address the public and the politicians with arguments. This means writing to the politicians and in newspapers and influence the wherever possible, like using Facebook etc.
SAFE: Please tell us more about your organisation.
BB: Our organization is driven by stroke injured people and our main issue is to work for stroke injured people. We are a nonprofit organization having approx. 1250 members spread all over Norway in 19 local organizations. We plan to establish more local organization, but we see also that we need to change our structure a bit in some places. Some of the local organizations cover a too large area and it is not possible for them to gather people from all over their area, so we may need to split some large organizations into smaller units.
Neuropathic Pain After Stroke
Dr Hege Ihle-Hansen, specialist in inner medicine and geriatrics at Oslo University hospital, Ullevål, told us that in follow-up after stroke a neuropathic pain is also mapped, and this is included in the national guidelines concerning follow-up 3 months after stroke.
Grethe Lunde, a stroke survivor, member of Norsk forening for slagrammede and SAFE Board member is one of many stroke survivors who live with neuropathic pain.
“How to live with muscle pain/neurological pain after 25 years as a stroke survivor? Well, I am really happy to be a knitter, as knitting often cuts the link to the “pain button” in our brain. It is a great way to disconnect from what is hurting. Knitting is also great fun and a really good tool for enhancing the mobility in your hands. Knitting distracts you from chronic pain. A study conducted by Harvard Medical School’s Mind and Body Institute, found that knitting lowers heart rate, by an average of 11 beats per minute, and induces an “enhanced state of calm, similar to that of yoga” concluded Grethe.

Photos by: Grethe Lunde Some of the knitting patterns that Grethe knitted recently.
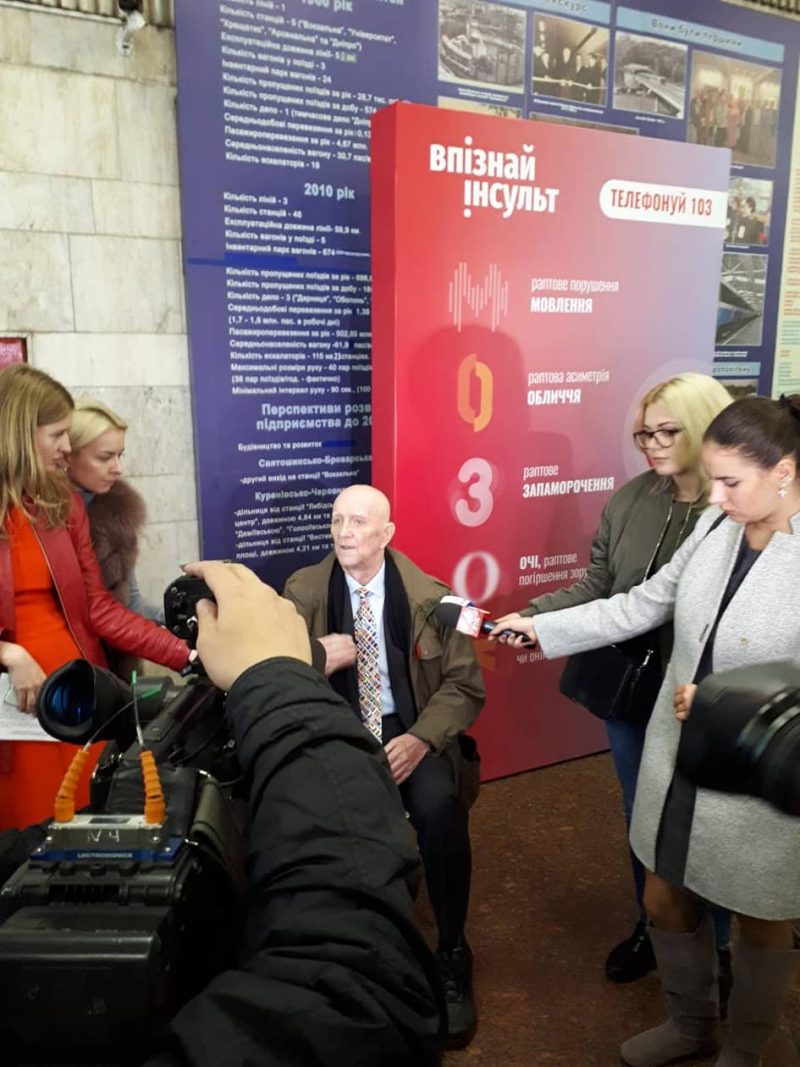


Jun 14, 2019
This week we spoke with leaders of two SAFE member organisations from Ukraine, Prof. Liliya Zviagina, MD, PhD, President of the stroke support organisation ‘Victory over Stroke’ and Dmitriy Gulyayev, MD, PhD, Director of publishing and research projects, Medical adviser of public subdivision, Ukrainian Anti-Stroke Association.
“I would say that in the information related to stroke and stroke care in Ukraine, provided by some specialists and even institutions, there is a lot of inaccuracies, mistakes, and even obvious and impertinent lie and falsifications” said Dmitriy Gulyayev at the very beginning of our conversation.

Dmitriy Gulyayev
SAFE: What is one issue related to the life after stroke in your country that you think needs special attention?
 DG: Current state of stroke care in Ukraine is poor, so it is not easy to pick just one problem. In my opinion, one of the major issues is that special needs of stroke survivors are neglected by the society and the government. Stroke survivors are isolated from public – physically (due to inaccessible public transportation, buildings etc.), and psychologically (as they are often ashamed of their disabilities). They are not in focus and are almost ‘invisible’ for the society. Despite the fact that virtually anyone in Ukraine has a family member or a friend who suffered a stroke, they do not realize how many stroke survivors there are in Ukraine, how challenging their life is, and how unfair the society and the government treat this huge sub-population – stroke survivors, their relatives and caregivers.
DG: Current state of stroke care in Ukraine is poor, so it is not easy to pick just one problem. In my opinion, one of the major issues is that special needs of stroke survivors are neglected by the society and the government. Stroke survivors are isolated from public – physically (due to inaccessible public transportation, buildings etc.), and psychologically (as they are often ashamed of their disabilities). They are not in focus and are almost ‘invisible’ for the society. Despite the fact that virtually anyone in Ukraine has a family member or a friend who suffered a stroke, they do not realize how many stroke survivors there are in Ukraine, how challenging their life is, and how unfair the society and the government treat this huge sub-population – stroke survivors, their relatives and caregivers.
Unfortunately, stroke survivors themselves rarely volunteer to share their experiences and challenges, and thus we are unable figure out the list of their priorities, and often have no other choice than initiating projects at our own discretion. Moreover, stroke survivors are not prepared to join their forces to speak up about their problems and the unmet needs. As a result, official institutions, take care of those who are younger, more mobile, more active, and who are shouting about themselves louder. Particularly by this reason, among others, for example, rather influential social movement “Patients of Ukraine” was established and is managed and promoted by activists of HIV/AIDS and hepatitis organizations, and stroke items are far out of their interest and attention.

Liliya Zviagina
 LZ: Stroke is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality death in Ukraine and is the main cause of disability in adults. Number of sufferers varies from 200 -300 per 100 000 population, depends on region. The main risk factors for stroke are well understood and include atherosclerosis and high blood pressure as well as bad habits. Stroke has a harmful impact on social and family life.
LZ: Stroke is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality death in Ukraine and is the main cause of disability in adults. Number of sufferers varies from 200 -300 per 100 000 population, depends on region. The main risk factors for stroke are well understood and include atherosclerosis and high blood pressure as well as bad habits. Stroke has a harmful impact on social and family life.
Quality of stroke service varies from region to region and depends on sometimes from personal activities and forces of doctors. To promote good service for stroke patients we have understand what is wrong and what we could to do in existing conditions.
Stroke service in Ukraine is only in the beginning of the way, people could not always access the services they need. I would like to stress on some common problems in Ukraine and what changed during last years.
1/ People are not aware about stroke;
2/ Not all people address in time to get help;
3/ Not enough stroke units;
4/ There are not insurance, and patients must pay for their treatment;
4/ Stroke patients get treatment in general neurological department
5/ Not so many departments use modern treatment (thrombolytic therapy and thrombectomy);
6/Not so many departments are equipped for monitoring vital parameters of stroke patients;
7/ Not so many departments have trained staff to perform all needs of stroke patients, particularly who has a dill with sufferers who have communications problems caused by stroke, such as aphasia;
8/ Not so many departments have multidisciplinary teams;
9/ Early and later rehabilitation are poorly organized;
10/ Not all stroke survivors and their carers are provided with the recommendation they need when they discharge from the hospital;
11/There are not system for observe patient during the first year;
12/ Not all patients are offered individual budgets or direct payments within the first six weeks of their returning home;
13 Not all people has a good knowledge of primary and secondary stroke prophylactic
SAFE: What would be the solution, i.e. what is your organisation’s position regarding this issue?
DG: Obviously, there is no magic wand to solve this deep social problem. We have to be ready for long-lasting, often thankless routine activities. We have to:
-widely distribute through different channels stories about stroke survivors’ life, needs, problems, solutions – not only in Ukraine, but in other countries with different level of social and economic development;
-build different platforms (both real and virtual) for communication of stroke survivors – peer-to-peer, and with surrounding world;
-involve stroke survivors into elaboration of stroke care on national, regional and local levels, encourage their active self-advocacy.
LZ: This can be summarized in couple of points:
1. The ministry of health declares some prevention measures; there is program -“Available medications”, which covered costs anti-hypertensive medicine, medicine to treat diabetes, …
2. The ministry of health proved protocol of ischemic stroke treatment N602 from 03/08/2012 which is act till now, should be revised according new trends, including thrombectomy
Over the last years the number of stroke units and thrombolytic therapy increased considerably as well as clinic where clot retrieving is available.
Despite of it we must improve these directions, which are help not only survive but return to social life.
SAFE: Please tell us more about your organisation
DG: The Ukrainian Anti-Stroke Association (UASA) is the All-Ukrainian nongovernmental organization established in 2004 with the purpose of integrating efforts of medical professionals, scientists, teaching staff of medical educational institutions, workers of social services, mass-media and people at large for improving the health care system in treating patients with stroke, primary and secondary stroke prevention, rehabilitation of patients after stroke and improving quality of medical and social help for patients who had stroke. Since its establishment, UASA is one of the most aggressively working Ukrainian NGOs in the field of medicine and health care, and the single organization totally devoted to stroke.
UASA elaborates, publishes and disseminates National Guidelines on stroke care, holds the most important Ukrainian scientific and education events for stroke physicians and allied health care professional, publishes as its official printed matter the single Ukrainian professional journal totally devoted to stroke “Sudynni Zakhvoryuvannya Golovnogo Mozku” (Cerebrovascular Diseases). For 4 years (2010-2013) UASA was publishing the Russian-language version of the “International Journal of Stroke” – the official printed matter of the World Stroke Organization – for all countries where Russian language is in use, including Russia. Several years ago, UASA has initiated and since then is a leader in the SUNEP – stroke unite nurses education project, which is very useful and successful not only in Ukraine, but in other countries of Eastern and Central Europe.
Main directions of work with general population are educational events for stroke survivors and their caregivers, educational materials for patients and general population, particularly the brochures on different aspects of stroke, “Guidebook on neurological diseases for laymen”, etc. The book “Stroke: Information for those who are concerned” has been re-published 8 times.
We fulfil wide educational activity in Facebook, and currently are on the way to finalize and publish the popular web-resource on stroke for general audience. UASA always was the principal organizer of the activities related to the World Stroke Day in Ukraine.
UASA is member of World Stroke Association and European Stroke Organization and is on the final stage of joining SAFE.
LZ: School for stroke survivors “Victory over stroke” was establish within Odessa neurological society in 2008, after visiting SAFE conference. We started with a small group of stroke survivors, trying to manage their life better, arranging some musical concerts, meetings and courses. We work and people help us as a volunteer. Since 2013 I become general neurologist of Odessa health department and from this time, I try to change the system of patient’s service and act more globally. We are working on many directions:
1.People information, (TV, meetings, newspapers)
2.Stroke prevention (patients and doctors)
3.We are involved in city program “Health” which let our patients get access to CT in acute stage for free and get three days treatment according to protocol, this year we have plane to open three stroke units (one is ready now)
4.Thrombolytic therapy will be paid by this program as well as thrombus retrieving.
5.There two telemedicine centers, where patients from the countryside have access for consultations
6.We teach doctors, mange local, national and international conferences.
7.Late rehabilitation center was open in one of Odessa clinic, where patients have accesses to improve their motor dysfunction, be adapt to the city and home environment
8.I joined school to University of third age, where people improved social life to study a lot of new subjects, computers, languages, tourist’s routes, where I teach people different medical questions, presented brochures, given to our organisation by SAFE, and presented new directions of stroke treatment, etc. This kind of activity play positive role, students of the university recognized stroke in one of the visitors and give help him immediately
9.Mortality after ischemic and haemorrhagic stroke decreased
Photo credits: Facebook (Roman Shwed, featured photo); profile photos of the interviewed persons: Personal archive













 DG: Current state of stroke care in Ukraine is poor, so it is not easy to pick just one problem. In my opinion, one of the major issues is that special needs of stroke survivors are neglected by the society and the government. Stroke survivors are isolated from public – physically (due to inaccessible public transportation, buildings etc.), and psychologically (as they are often ashamed of their disabilities). They are not in focus and are almost ‘invisible’ for the society. Despite the fact that virtually anyone in Ukraine has a family member or a friend who suffered a stroke, they do not realize how many stroke survivors there are in Ukraine, how challenging their life is, and how unfair the society and the government treat this huge sub-population – stroke survivors, their relatives and caregivers.
DG: Current state of stroke care in Ukraine is poor, so it is not easy to pick just one problem. In my opinion, one of the major issues is that special needs of stroke survivors are neglected by the society and the government. Stroke survivors are isolated from public – physically (due to inaccessible public transportation, buildings etc.), and psychologically (as they are often ashamed of their disabilities). They are not in focus and are almost ‘invisible’ for the society. Despite the fact that virtually anyone in Ukraine has a family member or a friend who suffered a stroke, they do not realize how many stroke survivors there are in Ukraine, how challenging their life is, and how unfair the society and the government treat this huge sub-population – stroke survivors, their relatives and caregivers.
 LZ: Stroke is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality death in Ukraine and is the main cause of disability in adults. Number of sufferers varies from 200 -300 per 100 000 population, depends on region. The main risk factors for stroke are well understood and include atherosclerosis and high blood pressure as well as bad habits. Stroke has a harmful impact on social and family life.
LZ: Stroke is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality death in Ukraine and is the main cause of disability in adults. Number of sufferers varies from 200 -300 per 100 000 population, depends on region. The main risk factors for stroke are well understood and include atherosclerosis and high blood pressure as well as bad habits. Stroke has a harmful impact on social and family life.



